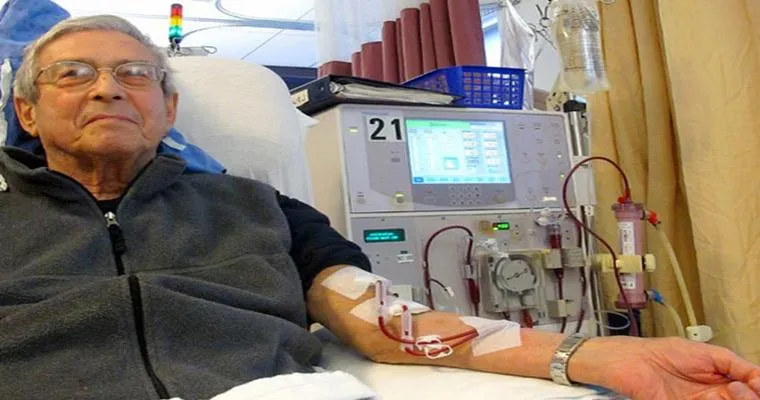
Dealing with "End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)" can be particularly challenging for an "89.5-year-old". As kidney function declines, it is essential to adopt a holistic approach to health and well-being. This article provides valuable advice for managing ESRD, focusing on diet, treatment options, emotional support, and lifestyle changes.
Understanding ESRD
End-Stage Renal Disease is the final stage of chronic kidney disease, where the kidneys can no longer function adequately. For elderly patients, the effects of ESRD can be compounded by other age-related health issues. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to understand the specific implications of ESRD and the available treatment options.
Dietary Considerations
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in managing ESRD. An "appropriate diet" can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some dietary tips:
1. "Limit Protein Intake": While protein is essential for health, excessive intake can put additional strain on the kidneys. Consult a dietitian to determine the right amount of protein.
2. "Control Sodium and Potassium": High sodium can lead to fluid retention and hypertension, while potassium levels must be monitored to avoid complications. Aim for low-sodium foods and discuss potassium limits with a healthcare provider.
3. "Stay Hydrated": Fluid intake may need to be restricted based on urine output and other health conditions. Always follow medical advice regarding fluid consumption.
4. "Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods": Incorporate fruits and vegetables that are low in potassium, along with whole grains and healthy fats. Consider foods rich in fiber to support digestive health.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment pathways for managing ESRD, and the best choice depends on individual health conditions and preferences:
1. "Dialysis": This is a common treatment for ESRD. There are two types: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Discuss with healthcare providers which option is suitable based on lifestyle and health status.
2. "Kidney Transplant": For eligible patients, a kidney transplant can significantly improve quality of life. It is essential to evaluate the risks and benefits of this option, especially in elderly patients.
Emotional and Social Support
Living with ESRD can lead to feelings of isolation or depression. It is essential to prioritize emotional well-being. Here are some strategies:
1. "Stay Connected": Maintain relationships with family and friends. Regular social interactions can provide emotional support and improve overall well-being.
2. "Seek Support Groups": Joining a support group for those with ESRD can be incredibly beneficial. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can provide comfort and practical advice.
3. "Consider Professional Help": If feelings of anxiety or depression arise, do not hesitate to seek help from a mental health professional. Therapy can provide coping strategies and emotional support.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating positive lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the quality of life. Here are some suggestions:
1. "Regular Physical Activity": Engage in gentle exercises, such as walking or stretching, to maintain mobility and improve overall health. Always consult a doctor before starting any new exercise routine.
2. "Prioritize Sleep": Quality sleep is vital for health, especially for those with chronic illnesses. Establish a calming bedtime routine to enhance sleep quality.
3. "Stay Informed": Educate yourself about ESRD and its management. Knowledge empowers patients and helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Conclusion
For an "89.5-year-old" living with "End-Stage Renal Disease", managing health requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary modifications, treatment options, emotional support, and lifestyle changes. By focusing on these aspects, individuals can lead a more fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by ESRD. Always work closely with healthcare providers to tailor the best plan for individual needs and circumstances.