The "shingles vaccine" is an important health intervention designed to protect against "herpes zoster", commonly known as shingles. Shingles is a painful rash caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox, and it can occur in individuals who have previously had chickenpox. Understanding the shingles vaccine, its benefits, and who should receive it is crucial for maintaining health, especially for older adults.
What is Shingles?
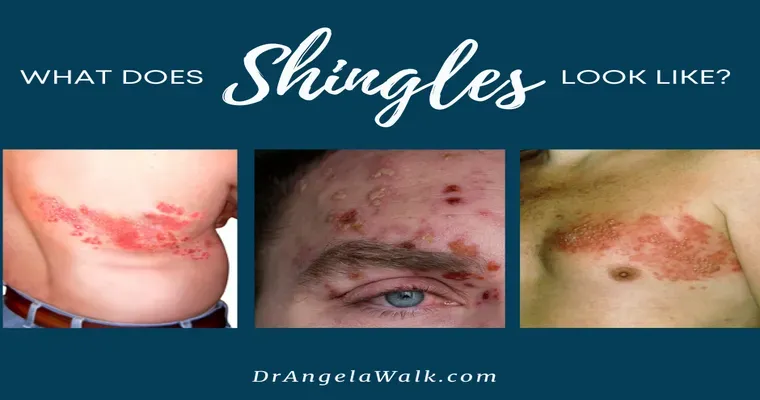
Shingles occurs when the varicella-zoster virus, which lies dormant in the body after a chickenpox infection, reactivates. This condition is characterized by a painful rash that can lead to severe discomfort and complications such as postherpetic neuralgia, which is lingering pain long after the rash has healed. The risk of developing shingles increases with age, making vaccination a vital consideration for older adults.
The Shingles Vaccine Options
There are two main types of shingles vaccines currently available: Zostavax and Shingrix.
"Zostavax": This is a live attenuated vaccine that has been used for several years. It is administered as a single injection and is recommended for adults aged 60 and older. However, its effectiveness diminishes over time.
"Shingrix": This is a newer, recombinant vaccine that has shown to be significantly more effective than Zostavax. The Shingrix vaccine is administered in two doses, typically given 2 to 6 months apart, and is recommended for adults aged 50 and older, regardless of their history with chickenpox or shingles.
Benefits of the Shingles Vaccine
Receiving the "shingles vaccine" provides several benefits:
1. "Reduced Risk of Shingles": Vaccination greatly decreases the likelihood of developing shingles.
2. "Decreased Severity": For those who do contract shingles after vaccination, the symptoms are often less severe.
3. "Prevention of Complications": Vaccination can help prevent complications associated with shingles, such as postherpetic neuralgia.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
The "shingles vaccine" is especially recommended for:
Adults aged 50 and older
Individuals with weakened immune systems
Those with a history of shingles
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if the vaccine is appropriate, particularly if you have specific health conditions or are on certain medications.
Possible Side Effects
Like any vaccine, the shingles vaccine can cause side effects, although most are mild and temporary. Common side effects include:
Pain at the injection site
Fatigue
Headaches
Muscle pain
Serious side effects are rare, but it is essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
The "shingles vaccine" is a crucial tool in preventing shingles and its associated complications. With options like Shingrix available, adults can significantly reduce their risk and enjoy better health as they age. If you are considering the shingles vaccine, speak with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your health needs. Protecting yourself from shingles is an important step toward maintaining overall well-being.