Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. Recognizing the "signs and symptoms" early can significantly impact the quality of life for both patients and caregivers. Understanding the available "treatments" is crucial for managing this complex condition.
Signs of Alzheimer's Disease
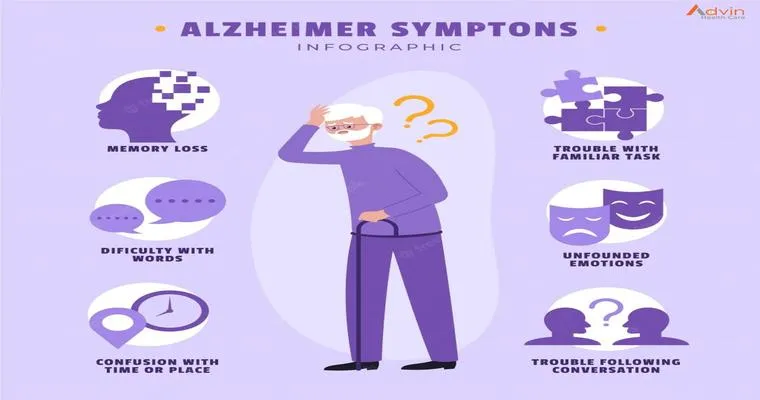
The signs of Alzheimer's disease often develop slowly and may vary from person to person. Common early signs include:
1. "Memory Loss": Frequently forgetting recent events, names, or conversations.
2. "Difficulty with Problem Solving": Struggling to develop or follow a plan or work with numbers.
3. "Confusion with Time or Place": Losing track of dates, seasons, and the passage of time.
4. "Difficulty Completing Familiar Tasks": Challenges in completing everyday tasks, such as driving to a known location or managing a budget.
5. "Changes in Mood and Personality": Experiencing mood swings, anxiety, or depression.
Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease
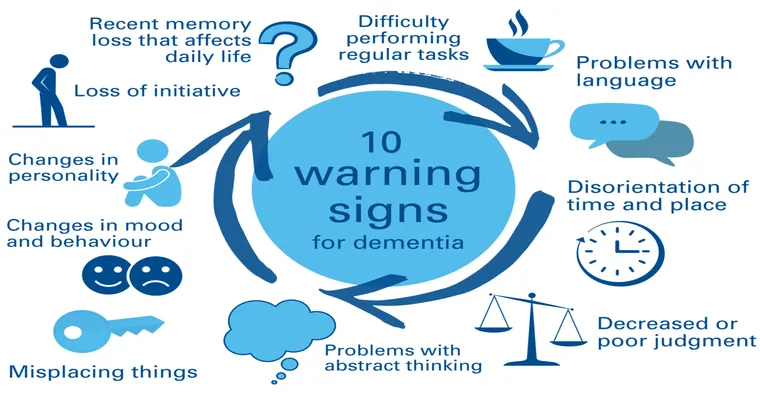
As Alzheimer's progresses, symptoms can become more severe. They may include:
1. "Increased Memory Loss": Forgetting important dates or events and relying heavily on memory aids.
2. "Communication Difficulties": Struggling to find the right words or following conversations.
3. "Disorientation": Becoming confused about time, place, or people.
4. "Poor Judgment": Making questionable decisions, particularly around finances or personal safety.
5. "Withdrawal from Social Activities": Avoiding social engagements and hobbies once enjoyed.
Treatments for Alzheimer's Disease
While there is currently no cure for Alzheimer's disease, several "treatments" may help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These treatments can be categorized into medications and non-pharmacological approaches.
Medications
1. "Cholinesterase Inhibitors": These drugs, such as donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine, may help improve memory and cognitive function in some individuals.
2. "Memantine": This medication is used to treat moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease and can help with memory, attention, and reasoning.
3. "Antidepressants": Managing symptoms of depression and anxiety can improve overall well-being.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
1. "Cognitive Stimulation Therapy": Engaging in activities that stimulate thinking and memory can be beneficial.
2. "Exercise": Regular physical activity can enhance mood and promote overall health.
3. "Social Engagement": Maintaining social connections can help reduce feelings of isolation and depression.
Conclusion
Early recognition of "Alzheimer's disease signs and symptoms" is vital for effective management. While current "treatments" cannot stop the progression of the disease, they can alleviate symptoms and enhance the quality of life for those affected. If you or a loved one are experiencing signs of Alzheimer's, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized care plan.