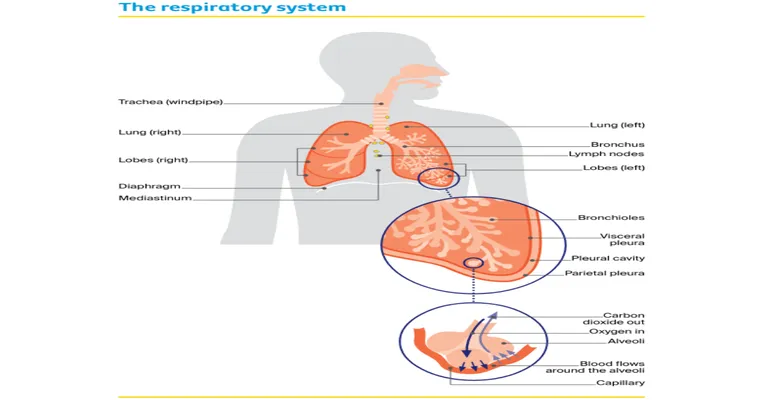
Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer worldwide, making it a significant health concern for many. This disease primarily affects the "lungs", leading to various symptoms and complications that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lung cancer is essential for early detection and effective management.
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is generally categorized into two main types: "non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)" and "small cell lung cancer (SCLC)". NSCLC is the most common type, accounting for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases. It is further divided into subtypes, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. On the other hand, SCLC is less common but tends to grow and spread more quickly, making it more aggressive.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of lung cancer, with "cigarette smoking" being the most significant. Inhaling tobacco smoke introduces numerous carcinogens into the lungs, increasing the likelihood of cancerous changes. Other risk factors include exposure to "secondhand smoke", "asbestos", radon gas, and certain chemical substances. Additionally, individuals with a family history of lung cancer or those with preexisting lung conditions are at a higher risk.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Recognizing the symptoms of lung cancer is crucial for early diagnosis. Common symptoms include a persistent cough that worsens over time, chest pain, difficulty breathing, weight loss, and coughing up blood. While these symptoms can be associated with other conditions, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if they persist.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing lung cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as chest X-rays and "CT scans", along with biopsy procedures to confirm the presence of cancerous cells. Early detection is vital, as it significantly impacts treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Treatment Options
Treatment for lung cancer depends on various factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatment modalities include "surgery", "radiation therapy", "chemotherapy", and targeted therapies. In some cases, immunotherapy may also be an option, helping to boost the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
Conclusion
In summary, lung cancer remains a major public health issue that requires awareness and understanding. By recognizing the risk factors and symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards early detection and treatment. Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding of lung cancer, promising better outcomes for those affected. If you or someone you know is at risk, consider regular screenings and consultations with healthcare professionals to stay informed and vigilant.