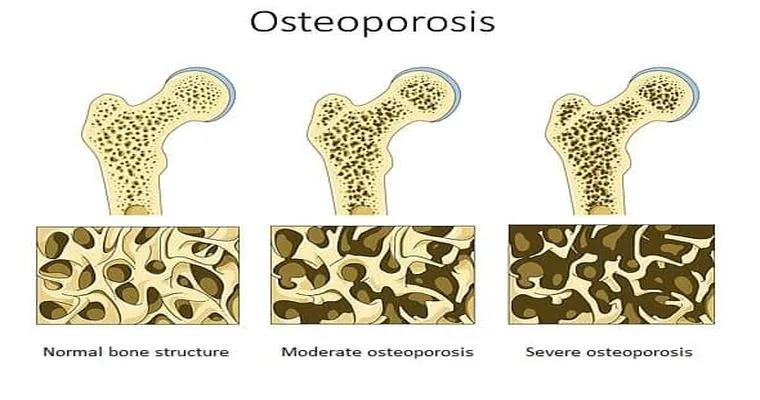
Osteoporosis is a "bone disease" characterized by decreased bone density and increased fragility, making bones more susceptible to fractures. This condition often develops silently over many years, frequently going unnoticed until a fracture occurs. Understanding the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for osteoporosis is crucial for prevention and management.
What Causes Osteoporosis?
The primary cause of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone resorption and bone formation. As we age, the body tends to lose more bone mass than it can replace. Several factors contribute to this condition, including "hormonal changes", particularly in women after menopause when estrogen levels drop significantly. Other causes include a sedentary lifestyle, inadequate "calcium" and "vitamin D" intake, and certain medical conditions or medications that can affect bone health.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Several "risk factors" increase the likelihood of developing osteoporosis. These include:
1. "Age:" The risk increases as you get older.
2. "Gender:" Women are at a higher risk than men, particularly post-menopause.
3. "Family History:" A family history of osteoporosis can increase your risk.
4. "Body Frame Size:" Smaller body frames may have a higher risk due to less bone mass.
5. "Lifestyle Factors:" Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can contribute to bone loss.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often termed a "silent disease" because it typically does not present symptoms until a fracture occurs. Common signs that may indicate osteoporosis include:
"Fractures" that occur more easily than expected, especially in the hip, spine, or wrist
A loss of height over time
A stooped posture or a noticeable curvature of the spine
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
To diagnose osteoporosis, healthcare providers often use a "bone density test", also known as a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. This test measures bone mineral density and helps determine the risk of fractures. The results are compared to a standard population to assess bone health.
Treatment and Management
While osteoporosis cannot be reversed, it can be managed effectively to reduce the risk of fractures. Treatment options include:
1. "Medications:" Bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and other drugs can help strengthen bones.
2. "Dietary Changes:" Increasing intake of calcium and vitamin D can support bone health.
3. "Exercise:" Weight-bearing and resistance training exercises can help build bone density.
4. "Lifestyle Modifications:" Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and ensuring a safe living environment can prevent falls and fractures.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a serious condition that requires awareness and proactive management. By understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to maintain their "bone health" and reduce the likelihood of fractures. Regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications can go a long way in preventing osteoporosis and ensuring a healthier future.