"Anemia in seniors" is a common yet often overlooked health issue that can significantly impact the quality of life. As people age, they may experience a decrease in red blood cell production, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Understanding the "causes", "symptoms", and "treatment options" for anemia is crucial for maintaining health in older adults.
Understanding Anemia in Seniors
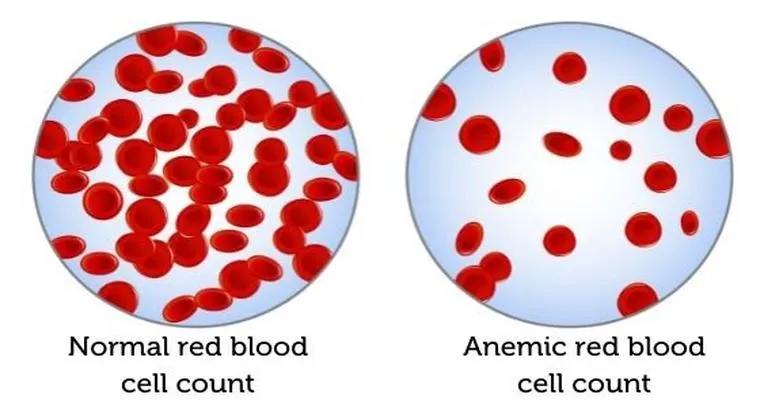
Anemia occurs when the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to the tissues. In seniors, this condition can be caused by various factors, including chronic diseases, nutritional deficiencies, and bone marrow disorders. The most common types of anemia found in older adults include iron-deficiency anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, and anemia of chronic disease.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of anemia in seniors is vital for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
"Fatigue": A noticeable lack of energy or extreme tiredness that doesn't improve with rest.
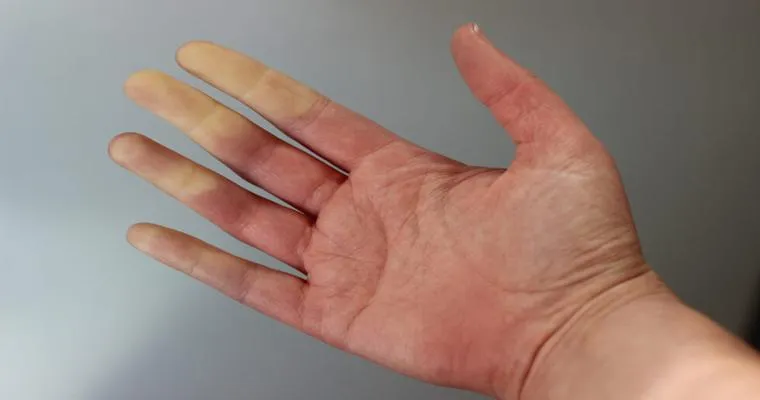
"Pale Skin": A noticeable change in skin tone, often appearing paler than usual.
"Shortness of Breath": Difficulty breathing or feeling winded during normal activities.
"Dizziness or Lightheadedness": Feeling faint or unsteady, especially when standing up quickly.
"Cold Hands and Feet": A sensation of coldness in extremities, which can be a sign of poor circulation.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of anemia in seniors. These include:
"Chronic Illnesses": Conditions such as chronic kidney disease, cancer, and inflammatory disorders can contribute to anemia.
"Poor Nutrition": A diet lacking essential nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and folate can lead to anemia.
"Medications": Certain medications can interfere with the body's ability to absorb nutrients, causing anemia.
Diagnosis
If you suspect anemia in a senior, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, a review of medical history, and blood tests to measure hemoglobin levels, red blood cell counts, and other relevant parameters.
Treatment Options
Treating anemia in seniors depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
1. "Dietary Changes": Increasing the intake of iron-rich foods such as red meat, beans, and leafy greens can help combat iron-deficiency anemia. Foods high in vitamin B12, like fish, eggs, and dairy products, are also beneficial.
2. "Supplements": In some cases, doctors may recommend iron supplements or vitamin B12 shots to correct deficiencies.
3. "Medications": If anemia is due to a chronic disease, treating the underlying condition may improve anemia symptoms.
4. "Blood Transfusions": In severe cases, a blood transfusion may be necessary to quickly increase red blood cell levels.
5. "Monitoring and Adjustments": Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for managing anemia effectively, especially as the individual's health needs may change over time.
Conclusion
Anemia in seniors is more than just a minor health concern; it can significantly affect overall well-being and functionality. By being aware of the "symptoms", understanding the "risk factors", and knowing the "treatment options", caregivers and seniors can work together to manage this condition effectively. Early detection and appropriate management can lead to a better quality of life, allowing seniors to remain active and engaged in their daily activities. If you notice any signs of anemia in yourself or a loved one, do not hesitate to seek medical advice.