"Aphasia" is a communication disorder that affects a person's ability to express and understand language. It is often caused by "brain injury", particularly from strokes, traumatic brain injuries, or neurological conditions. Individuals diagnosed with aphasia may struggle with speaking, writing, and understanding both spoken and written language. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for aphasia, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
Understanding Aphasia
Aphasia results from damage to the areas of the brain responsible for language processing. The most common cause is a stroke, which can disrupt blood flow to vital brain regions. Other potential causes include head injuries, brain tumors, infections, or progressive neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's.
There are several types of aphasia, each characterized by different symptoms and communication challenges. The two main categories are non-fluent and fluent aphasia. Non-fluent aphasia, often associated with Broca's area damage, makes it difficult for individuals to form complete sentences, leading to halting or broken speech. In contrast, fluent aphasia, linked to Wernicke's area damage, allows individuals to speak with normal grammar and speed, but their words may lack meaning or be nonsensical.
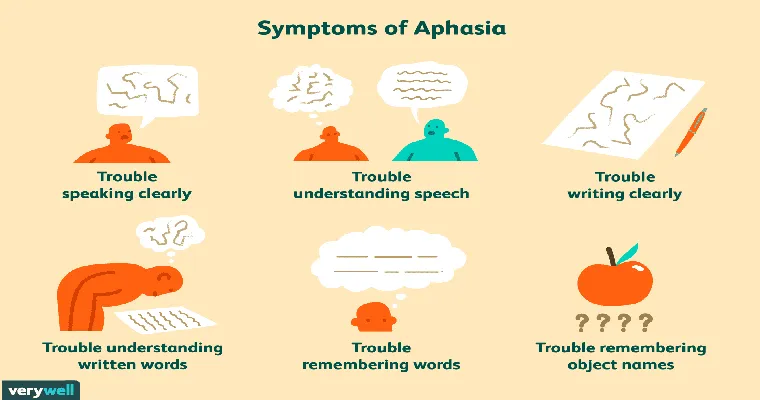
Symptoms of Aphasia
The symptoms of aphasia can vary greatly depending on the extent and location of the brain injury. Common signs include:
Difficulty finding the right words or forming sentences
Substituting words or using made-up words
Trouble understanding spoken or written language
Difficulty with reading comprehension and writing
These symptoms can profoundly impact an individual's ability to communicate, leading to frustration and social withdrawal.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosing aphasia typically involves a thorough evaluation by a speech-language pathologist (SLP). The assessment may include a variety of tests to measure language skills, including speaking, listening, reading, and writing. The SLP will also consider the individual's medical history and the specifics of their brain injury.
Treatment Options
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for aphasia, various treatment options can help individuals regain their communication skills. Speech therapy is the cornerstone of aphasia treatment. An SLP will work with patients on exercises that target specific language deficits. Therapy may include:
Word retrieval exercises
Sentence construction practice
Reading and writing activities
Group therapy sessions for social interaction
In some cases, technology and communication devices can assist individuals with aphasia in expressing themselves more effectively. Support groups and family education are also crucial, as they can help create a positive environment for recovery.
Coping with Aphasia
Living with aphasia can be challenging, not just for the affected individuals but also for their families. It’s essential to foster an understanding and supportive atmosphere. Encouraging communication, being patient, and using simple language can significantly aid in the recovery process.
Conclusion
Aphasia is a complex condition resulting from "brain injury" that can severely affect communication abilities. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for those affected by aphasia and their loved ones. With proper intervention, many individuals can improve their language skills and lead fulfilling lives. If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of aphasia, seeking help from a qualified speech-language pathologist is the first step toward recovery.