Breast cancer is a serious health concern that affects millions of women and men worldwide. Understanding the "signs", "symptoms", and "treatments" available for breast cancer is crucial for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable information to help individuals recognize the importance of awareness and timely action.
Signs of Breast Cancer
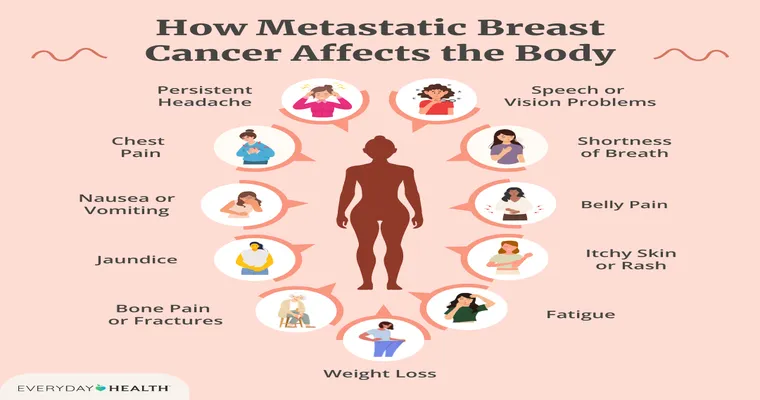
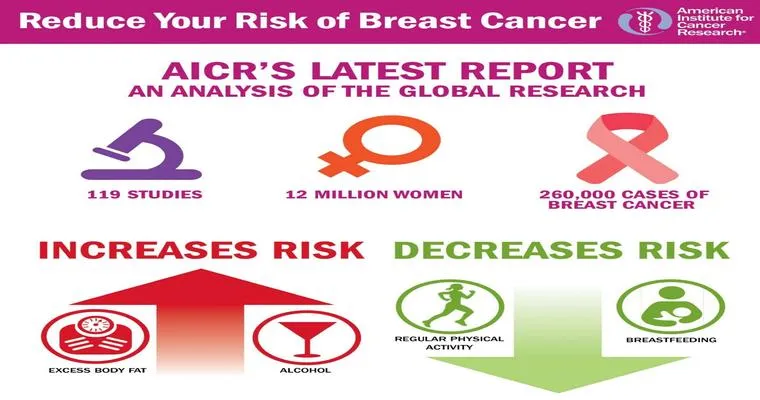
Early detection of breast cancer significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. Some common "signs" to watch for include:
"Lumps" or masses in the breast or underarm area
Changes in the "size" or "shape" of the breast
Unexplained "swelling" or "thickening" of breast tissue
Changes in the "skin" of the breast, such as dimpling or puckering
"Nipple discharge", especially if it is bloody or occurs without squeezing the nipple
It is essential to perform regular self-examinations to identify any unusual changes and consult a healthcare professional if any of these signs are present.
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
In addition to the signs mentioned above, various "symptoms" may indicate breast cancer. These can include:
Persistent pain in the breast or nipple
Changes in the "nipple", such as inversion or redness
A "rash" or irritation on the breast or nipple
Swollen lymph nodes in the underarm or collarbone area
Symptoms can vary from person to person, and some individuals may experience no symptoms at all in the early stages. Regular medical check-ups and mammograms are essential for early detection.
Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
If breast cancer is suspected, a healthcare provider may recommend several tests for a definitive diagnosis. These tests can include:
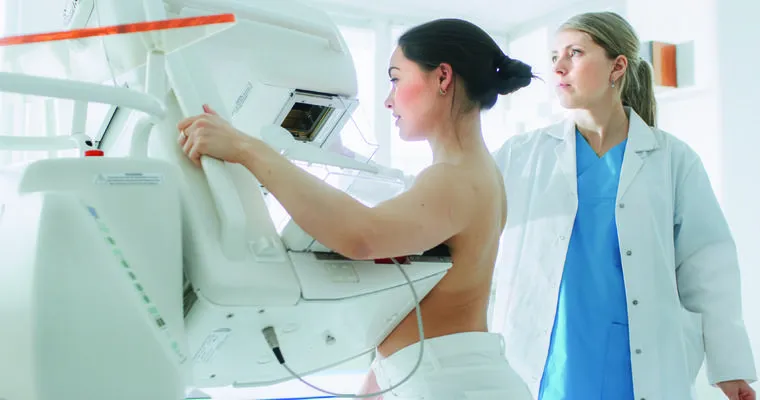
"Mammograms", which are X-ray images of the breast
"Ultrasounds" to assess the characteristics of a lump
"Biopsies", where a small sample of breast tissue is examined for cancer cells
Early diagnosis is key to improving treatment outcomes, so it is crucial to follow recommended screening guidelines.
Treatments for Breast Cancer
Once diagnosed, several "treatment" options are available, depending on the type and stage of breast cancer. Common treatment modalities include:
"Surgery": This may involve a lumpectomy (removal of the tumor) or mastectomy (removal of one or both breasts).
"Radiation therapy": High-energy waves are used to target and kill cancer cells.
"Chemotherapy": Powerful drugs are administered to destroy cancer cells or stop their growth.
"Hormonal therapy": This treatment blocks hormones that fuel certain types of breast cancer.
"Targeted therapy": This involves using drugs that specifically target cancer cell characteristics.
The choice of treatment is highly individualized and may involve a combination of therapies. It is essential for patients to discuss options thoroughly with their healthcare team.
Conclusion
Breast cancer remains a significant health issue, but awareness of its "signs", "symptoms", and "treatments" can empower individuals to take proactive measures. Regular screenings, self-examinations, and consultations with healthcare providers are vital for early detection and effective treatment. By staying informed and vigilant, we can enhance our chances of combating this disease and improving outcomes for those affected.