Choking can be a serious concern for individuals living with "dementia", as cognitive decline may impair their ability to swallow effectively. Caregivers and family members often worry about the "risks of choking", which can lead to "life-threatening situations". Understanding the challenges associated with "dementia" and swallowing difficulties is essential for providing appropriate support and ensuring safety during mealtime.
Understanding the Connection Between Dementia and Choking
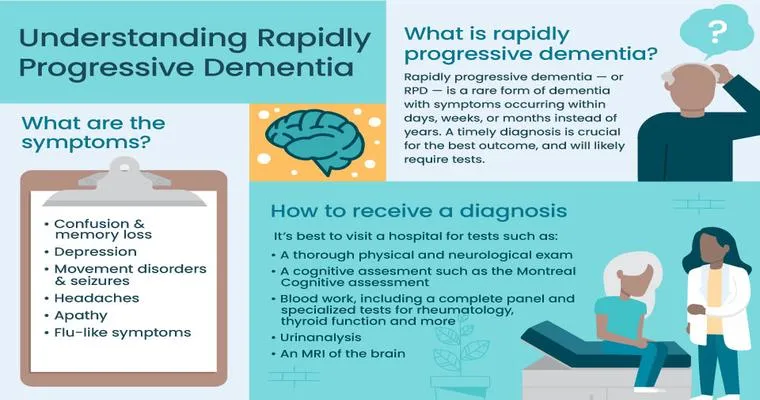
Dementia affects a person's cognitive functions, including memory, reasoning, and judgment. As the disease progresses, individuals may struggle with recognizing food, managing utensils, and properly chewing and swallowing. These challenges can significantly increase the risk of "choking" during meals.
Signs of Swallowing Difficulties
It is crucial for caregivers to be aware of signs that indicate a person with "dementia" may have trouble swallowing. Common symptoms include:
Frequent coughing or choking while eating
Gurgling or wet voice after eating
Food or liquid leaking from the mouth
Difficulty managing food textures
Recognizing these signs early can help prevent choking incidents and allow for timely interventions.
Tips for Safe Eating
To mitigate the risk of choking, caregivers can implement several strategies to create a safer eating environment for individuals with "dementia":
1. "Modify Food Textures": Offer softer foods that are easier to chew and swallow. Pureed foods, mashed potatoes, and finely chopped meats can be good options.
2. "Encourage Small Bites": Remind individuals to take small bites and chew thoroughly before swallowing. This can help reduce the risk of choking.
3. "Maintain a Calm Environment": Eliminate distractions during mealtime. A calm and quiet setting can help individuals focus on eating and swallowing.
4. "Stay with the Person During Meals": Caregivers should supervise meals to monitor for any signs of choking and provide immediate assistance if necessary.
5. "Use Adaptive Utensils": Consider using specially designed utensils that are easier to grip, allowing individuals to feed themselves more effectively.
Know How to Respond in an Emergency
Even with precautions in place, choking incidents can still occur. It is vital for caregivers to be prepared. Here are steps to take if someone is choking:
"Assess the Situation": Determine if the person can cough or speak. If they can, encourage them to keep coughing to dislodge the food.
"Call for Help": If the person cannot cough, speak, or breathe, call emergency services immediately.
"Perform Heimlich Maneuver": If trained, perform the Heimlich maneuver to help expel the object causing the choking.
Consult Healthcare Professionals
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for managing "dementia" and its associated challenges. Speech therapists can offer valuable guidance on swallowing techniques and dietary modifications tailored to the individual's needs.
Conclusion
Choking poses a significant risk for individuals living with "dementia", but with proper precautions and awareness, caregivers can help ensure safer mealtimes. By modifying food textures, maintaining a calm environment, and being prepared for emergencies, families can reduce the likelihood of choking incidents and provide a more enjoyable dining experience for their loved ones. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support tailored to individual needs.