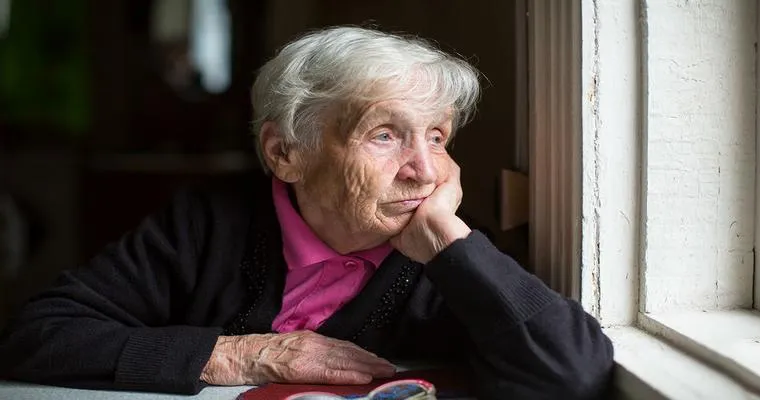
The "epidemic of loneliness" among "seniors" has become a pressing concern in today's society. With an increasing number of elderly individuals living alone or in isolation, the emotional and physical consequences of loneliness can be devastating. Understanding the underlying causes and implementing effective strategies to combat loneliness is essential for improving the quality of life for our aging population.
Understanding Loneliness in Seniors
Loneliness is not merely the absence of companionship; it is a profound emotional experience that can lead to various health issues. Many "seniors" face significant life changes, such as retirement, the loss of a spouse, or physical limitations, which can contribute to feelings of isolation. Furthermore, societal shifts have resulted in an increased number of older adults living alone, exacerbating this issue.
The Health Implications of Loneliness
Research has shown that prolonged loneliness can have serious health implications for "seniors". It is linked to a higher risk of various conditions, including depression, anxiety, heart disease, and even cognitive decline. The impact of loneliness on mental health cannot be overlooked, as it can lead to a downward spiral of emotional distress and physical ailments.
Strategies to Combat Loneliness
1. "Encourage Social Engagement": Creating opportunities for "seniors" to connect with others is vital. Community centers, senior clubs, and local events can provide a platform for social interaction. Encouraging participation in group activities, such as exercise classes or art workshops, can foster friendships and reduce feelings of isolation.
2. "Utilize Technology": In today's digital age, technology can play a crucial role in combating loneliness. Teaching "seniors" how to use video calling apps, social media, and online forums can help them stay connected with family and friends, even if they are physically distant.
3. "Volunteer Programs": Engaging "seniors" in volunteer work can provide a sense of purpose and community connection. Programs that match older adults with local organizations allow them to contribute their skills and experience, enhancing their social networks while making a positive impact.
4. "Pet Therapy": The companionship of pets can significantly alleviate feelings of loneliness. Many "seniors" find comfort in the presence of animals, and programs that promote pet adoption or therapy animals can be beneficial for mental well-being.
5. "Regular Check-Ins": Family members and caregivers should prioritize regular communication with "seniors" to ensure they feel valued and connected. Simple phone calls, texts, or visits can brighten their day and reinforce their support system.
Conclusion
Combatting the "epidemic of loneliness" in "seniors" requires a multi-faceted approach that involves community support, technology, and personal connections. By fostering an environment that promotes social engagement and emotional well-being, we can significantly improve the lives of our elderly population. It is crucial for society to recognize the impact of loneliness and take proactive steps to ensure that no senior has to face this journey alone. Together, we can create a more connected and compassionate world for our aging loved ones.