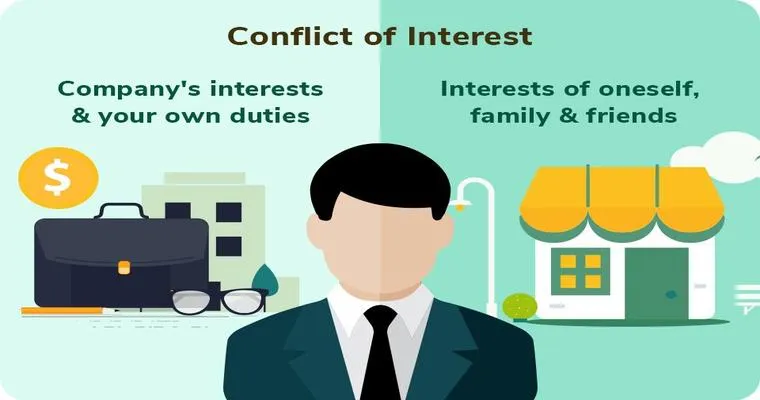
In today's complex world, "conflicts of interest" have become a significant concern in various fields, including "business", "law", and "government". A conflict of interest arises when an individual's personal interests interfere, or appear to interfere, with their professional obligations. These situations can lead to ethical dilemmas and may undermine public trust, making it essential for organizations and individuals to recognize and address these conflicts effectively.
What Are Conflicts of Interest?
A conflict of interest occurs when a person in a position of authority has competing interests that could impair their decision-making. This can happen in numerous scenarios, such as when a corporate executive has financial stakes in a competing company, or when a public official makes decisions that could benefit their personal investments. Understanding the various forms of conflicts of interest is crucial for maintaining integrity in professional environments.
Types of Conflicts of Interest
Conflicts of interest can be categorized into several types, including:
1. "Financial Conflicts": Involves situations where financial interests may affect objectivity. For example, a board member of a nonprofit organization may have a financial interest in a company that the organization is considering for a contract.
2. "Personal Conflicts": These occur when personal relationships influence professional decisions. For instance, hiring a family member for a position within a company can lead to questions about fairness and bias.
3. "Professional Conflicts": Professionals like lawyers or doctors may face dilemmas when representing clients or patients with conflicting interests. This can jeopardize the duty of loyalty they owe to each party.
4. "Organizational Conflicts": These arise when an organization’s interests conflict with those of its employees or stakeholders. An example would be a company prioritizing profits over employee well-being.
Consequences of Conflicts of Interest
Failing to address conflicts of interest can have severe repercussions, such as:
"Legal Ramifications": Many industries have specific laws and regulations governing conflicts of interest. Violations can lead to legal actions and penalties.
"Reputation Damage": Organizations or individuals that do not manage conflicts effectively may face public backlash, leading to loss of trust and credibility.
"Internal Strife": Conflicts can create divisions within teams, leading to a toxic work environment and decreased morale.
How to Manage Conflicts of Interest
Organizations and individuals can adopt several strategies to effectively manage conflicts of interest:
1. "Disclosure": Transparency is key. Individuals should disclose any potential conflicts to relevant parties, allowing for informed decision-making.
2. "Policies and Procedures": Establishing clear organizational policies regarding conflicts of interest can help create a culture of accountability.
3. "Training and Education": Regular training sessions on recognizing and managing conflicts of interest can empower employees to act ethically.
4. "Independent Oversight": In some cases, involving a third party to review decisions can help mitigate biases and enhance objectivity.
Conclusion
Conflicts of interest are an unavoidable aspect of professional life, but they need not derail careers or organizations. By understanding the different types of conflicts and implementing effective management strategies, individuals and companies can uphold ethical standards and maintain trust with stakeholders. Awareness and proactive measures are essential in navigating the complexities of conflicts of interest in any professional setting.