Dementia is a complex and challenging condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Among the various symptoms associated with "dementia", one particularly distressing phenomenon is known as "sundowning". This term refers to a behavioral pattern where individuals with dementia experience increased confusion, agitation, and anxiety during the late afternoon and evening hours. Understanding the connection between dementia and sundowners is crucial for caregivers and families aiming to provide effective support and care for their loved ones.
Sundowners syndrome typically manifests in those with "Alzheimer's disease" and other forms of dementia. As daylight fades, individuals may exhibit signs of restlessness, irritability, and even hallucinations. Caregivers often find that familiar routines can be disrupted by this phenomenon, leading to heightened emotional distress for both the individual and their support network.
The exact causes of sundowning are not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to this behavior. Changes in the body’s internal clock, fatigue, and the presence of shadows or dim lighting can all trigger increased confusion in individuals with dementia. Additionally, the lack of social interaction during the evening hours can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and anxiety.
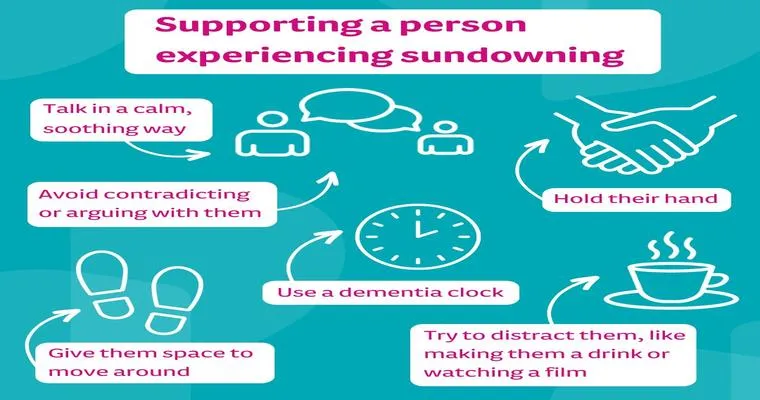
To manage sundowning effectively, caregivers can implement various strategies. Creating a calm and soothing environment is essential. Soft lighting, gentle music, and familiar objects can help to reduce agitation. Establishing a consistent daily routine that includes stimulating activities during the day can also minimize the likelihood of confusion in the evening.
Another key aspect in managing sundowners is ensuring that the individual is getting adequate rest. Fatigue can significantly worsen symptoms, so encouraging regular naps and ensuring a good night’s sleep can be beneficial. Caregivers should also be aware of the triggers that lead to sundowning episodes and work to mitigate them when possible.
Communication is also critical. Speaking in a calm and reassuring manner can help ease anxiety. Using simple language and providing clear instructions can guide individuals through their evening routine without overwhelming them.
For those providing care for individuals experiencing sundowning, it is important to practice self-care. Caregiving can be physically and emotionally taxing, and finding support for oneself is crucial to maintaining the necessary patience and resilience to manage challenging behaviors.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between "dementia" and "sundowners" is vital for effective care. By recognizing the signs and implementing supportive strategies, caregivers can help reduce the impact of sundowning on their loved ones. With compassion, patience, and the right approaches, it is possible to create a more peaceful and manageable evening routine for individuals affected by dementia.