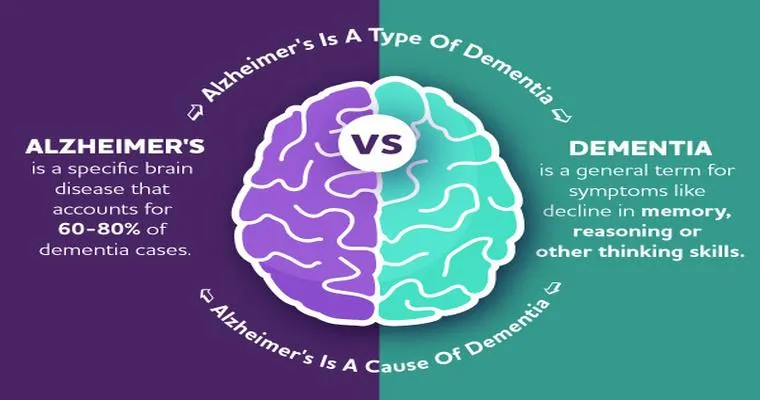
When caring for individuals with "dementia", it is not uncommon for caregivers and family members to perceive certain behaviors as "manipulation". However, understanding the underlying reasons for these actions is crucial for providing appropriate care and support. Dementia can cause significant changes in behavior and cognition, leading to confusion, frustration, and emotional distress for both the individual and those around them. In this article, we will explore how dementia behavior can be misunderstood and offer insights into effective caregiving strategies.
Individuals with dementia may exhibit "manipulative behaviors" that can be challenging for caregivers to interpret. These behaviors often stem from cognitive decline, memory loss, and difficulties in communication. For instance, a person with dementia may repeatedly ask the same question or insist on doing something despite being told otherwise. While this can seem like a tactic to gain attention or control, it is essential to recognize that these actions are often driven by confusion and anxiety rather than intentional manipulation.
One of the most common misconceptions is that individuals with dementia are aware of their actions and are deliberately trying to manipulate their caregivers. In reality, many of these behaviors arise from unmet needs or a lack of understanding of their surroundings. For example, a person may become agitated or aggressive when they feel overwhelmed or frightened. Recognizing these triggers can help caregivers respond in a compassionate and effective manner.
Effective communication is key when dealing with perceived "manipulative behaviors" in individuals with dementia. Caregivers should strive to maintain a calm and reassuring demeanor, using simple language and clear instructions. This approach can help reduce confusion and create a more supportive environment. Additionally, it is important to validate the individual’s feelings, even if their actions seem irrational. Acknowledging their emotions can help de-escalate difficult situations and foster a sense of trust.
In some cases, behavioral changes may also be linked to physical discomfort or medical issues. Regular health check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers can help identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the behavior. Addressing these issues can lead to improvements in the individual’s overall well-being and reduce instances of perceived manipulation.
Another effective strategy is to establish a consistent routine. Individuals with dementia often find comfort in familiarity, and a predictable schedule can help alleviate anxiety and confusion. Caregivers should incorporate activities that the individual enjoys and ensure they have opportunities for social interaction and engagement. This can lead to a more positive emotional state and reduce the likelihood of challenging behaviors.
In conclusion, while "dementia behavior" can sometimes appear to be manipulation, it is essential to approach these situations with empathy and understanding. By recognizing the underlying causes of these behaviors and employing effective caregiving strategies, caregivers can create a more supportive environment for individuals with dementia. Building trust, maintaining open communication, and addressing physical and emotional needs are all vital components of compassionate care. Ultimately, understanding the complexities of dementia can help bridge the gap between perception and reality, leading to improved outcomes for everyone involved.