Dementia with Behavioral Disturbances is a complex condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This form of "dementia" not only impacts cognitive functioning but also leads to significant "behavioral disturbances". Understanding the various "behaviors", "causes", and "types" associated with this condition is crucial for caregivers, health professionals, and families. In this article, we will explore the different facets of dementia with behavioral disturbances to provide a comprehensive overview.
Understanding Dementia and Behavioral Disturbances
Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of conditions characterized by the decline in cognitive function, which affects memory, thinking, and social abilities. When behavioral disturbances occur, they can manifest in numerous ways, including aggression, agitation, depression, and even psychotic symptoms like hallucinations. These behaviors can be distressing not only for the affected individual but also for caregivers and family members.
Common Behaviors in Dementia with Behavioral Disturbances
Individuals suffering from dementia may exhibit a variety of challenging behaviors, which can be categorized into several types:
1. "Aggression": This may involve verbal outbursts, physical violence, or throwing objects. Such behaviors often stem from frustration or an inability to communicate needs effectively.
2. "Agitation": This includes restlessness and the inability to sit still, which can lead to pacing, fidgeting, or engaging in repetitive movements.
3. "Depression": Many individuals with dementia experience feelings of sadness or hopelessness, which can manifest as withdrawal from activities or social interactions.
4. "Hallucinations and Delusions": Some patients may see or hear things that are not present, leading to confusion and fear.
5. "Wandering": This behavior involves individuals moving around aimlessly, which can pose significant safety risks.
Causes of Behavioral Disturbances in Dementia
Understanding the causes of behavioral disturbances is essential for effective management. Several factors may contribute to these behaviors, including:
1. "Neurological Changes": The brain undergoes significant changes due to dementia, affecting areas responsible for behavior and emotional regulation.
2. "Environmental Triggers": Changes in surroundings or routine can lead to confusion and agitation. Loud noises, too many people, or unfamiliar settings can trigger behavioral disturbances.
3. "Physical Discomfort": Pain, fatigue, or other medical conditions can exacerbate behavioral issues. It is crucial to assess physical health to address underlying discomfort.
4. "Communication Barriers": As cognitive abilities decline, individuals may struggle to express their needs, leading to frustration and behavioral outbursts.
5. "Psychological Factors": Depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions can also play a significant role in behavioral disturbances.
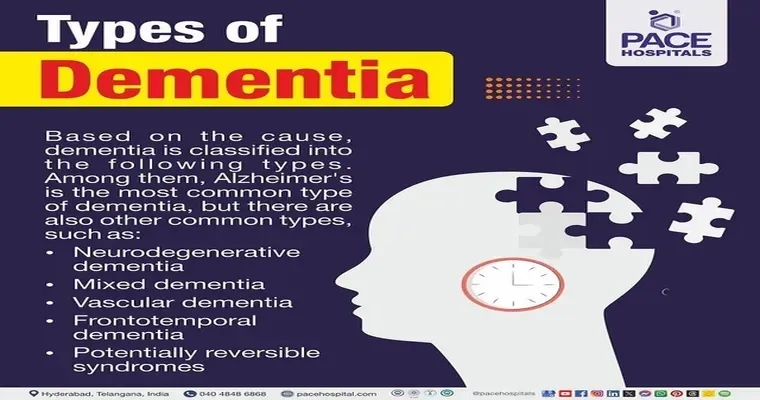
Types of Dementia Associated with Behavioral Disturbances
Several types of dementia are particularly known for their association with behavioral disturbances:
1. "Alzheimer's Disease": The most common form of dementia, Alzheimer's often leads to memory loss, confusion, and a range of behavioral issues.
2. "Frontotemporal Dementia": This type primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes, leading to significant changes in personality and behavior, often including inappropriate social behaviors.
3. "Vascular Dementia": Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, vascular dementia can result in mood swings and sudden changes in behavior.
4. "Lewy Body Dementia": Characterized by visual hallucinations and fluctuations in alertness, this type often leads to significant behavioral challenges.
5. "Mixed Dementia": Many individuals may experience more than one type of dementia, further complicating behavioral manifestations.
Managing Behavioral Disturbances
Managing behavioral disturbances in individuals with dementia requires a multifaceted approach. Caregivers should focus on:
1. "Creating a Calm Environment": Reducing noise and clutter can help minimize agitation.
2. "Establishing Routines": Consistent daily routines can provide a sense of security and reduce confusion.
3. "Effective Communication": Using simple language and maintaining eye contact can help bridge communication gaps.
4. "Monitoring Physical Health": Regular medical check-ups can help identify and address any underlying health issues contributing to behavioral changes.
5. "Seeking Professional Help": In some cases, medication or therapy may be necessary to manage severe behaviors effectively.
Conclusion
Dementia with Behavioral Disturbances is a challenging condition that requires careful understanding and management. By recognizing the behaviors, causes, and types associated with this form of dementia, caregivers and families can better support affected individuals. With appropriate strategies and interventions, it is possible to improve the quality of life for both individuals with dementia and their caregivers.