Bed wetting, also known as nocturnal enuresis, is a condition that can significantly impact the quality of life for the elderly. It is often overlooked or dismissed as a normal part of aging, but it is crucial to understand that "bed wetting in the elderly" can stem from various underlying health issues. Proper "diagnosis" and "treatment" are essential to address this sensitive issue and to improve the overall well-being of affected individuals.
Understanding Bed Wetting in the Elderly
Bed wetting in older adults can result from a combination of physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors. Some common causes include urinary tract infections (UTIs), medications that affect bladder control, neurological disorders, and cognitive impairments such as dementia. Additionally, factors like "fluid intake" before bedtime, sleep apnea, and depression can exacerbate the condition.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Diagnosing bed wetting in the elderly requires a comprehensive approach. A healthcare provider will typically begin with a thorough medical history and a physical examination. They may also conduct tests, such as urine analysis, to rule out infections or other underlying conditions. It is essential to understand the patient's "lifestyle", including their "diet", fluid intake, and any medications they are taking. Keeping a "bladder diary" can also provide valuable insights into patterns and potential triggers.
Treatment Options
Once a proper diagnosis is made, various "treatment options" are available to manage bed wetting in the elderly. These options can include:
1. "Lifestyle Modifications": Encouraging patients to limit fluid intake in the evening, especially caffeine and alcohol, can help reduce the likelihood of bed wetting. Establishing a regular bathroom routine can also be beneficial.
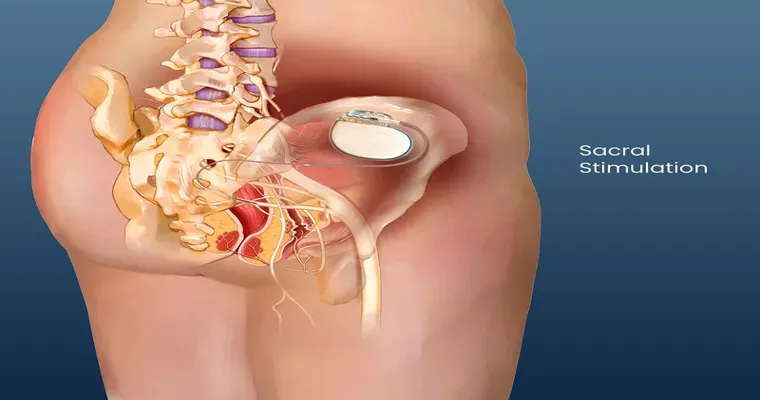
2. "Medications": Depending on the underlying cause, doctors may prescribe medications that help improve bladder control or address any contributing health issues. Anticholinergics, desmopressin, and bladder relaxants are some examples of medications that may be used.
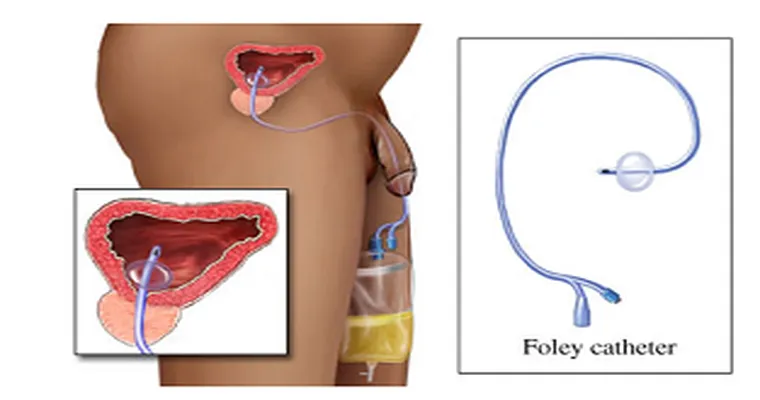
3. "Absorbent Products": In some cases, using absorbent products such as adult diapers or bed pads can provide comfort and protect against embarrassment. While this does not treat the underlying issue, it can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
4. "Behavioral Therapies": Techniques such as bladder training and pelvic floor exercises can help strengthen the bladder muscles and improve control. Additionally, cognitive-behavioral therapy may be beneficial for those dealing with anxiety or depression related to bed wetting.
5. "Addressing Underlying Conditions": Treating any underlying health issues, such as managing diabetes or addressing prostate problems in men, can also help alleviate bed wetting symptoms.
Conclusion
Bed wetting in the elderly is a common yet often neglected issue that can greatly affect an individual's dignity and self-esteem. By understanding the "causes", seeking an accurate "diagnosis", and exploring various "treatment options", caregivers and healthcare providers can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Awareness and open communication about this condition are vital to ensure that the elderly receive the compassionate care they deserve. If you or someone you know is experiencing bed wetting, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to discuss the best course of action.