When it comes to "diagnosing breathing issues", understanding whether the problem lies with the "heart" or the "lungs" is crucial for effective treatment. Both organs play vital roles in our respiratory system, and their functions are closely linked. In this article, we will explore the various symptoms, diagnostic methods, and potential conditions associated with breathing difficulties, helping you navigate the complexities of respiratory health.
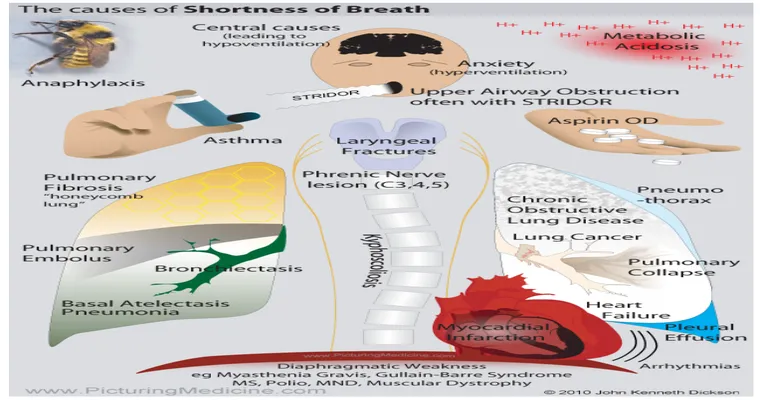
Breathing difficulties can manifest in numerous ways, including shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, or a feeling of tightness in the chest. These symptoms can be indicative of various underlying conditions. It is essential to distinguish between "pulmonary" issues that originate in the lungs and "cardiac" concerns that arise from heart problems. This distinction is vital, as the treatment approaches for lung diseases differ significantly from those for heart-related issues.
Recognizing Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing the source of breathing issues is to recognize the symptoms accurately. For instance, "lung-related symptoms" often include persistent cough, phlegm production, and a feeling of constriction in the chest. Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia are common pulmonary disorders that can cause these symptoms. On the other hand, "heart-related symptoms" may present as chest pain, palpitations, fatigue, or swelling in the legs and ankles. Heart failure, arrhythmias, and coronary artery disease are examples of cardiac conditions that could lead to breathing difficulties.
Diagnostic Methods
Once symptoms are identified, healthcare professionals will employ various "diagnostic methods" to determine the root cause of the breathing issues. Common diagnostic tests include:
1. "Physical Examination": A thorough physical exam allows doctors to assess breathing patterns and listen for abnormal lung sounds using a stethoscope.
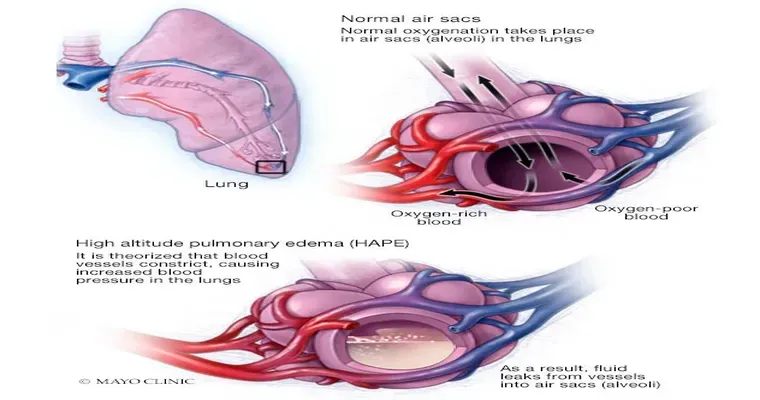
2. "Imaging Tests": Chest X-rays or CT scans can help visualize the lungs and heart, revealing issues such as fluid accumulation, lung infections, or structural abnormalities.
3. "Pulmonary Function Tests": These tests measure the lungs' capacity and airflow, helping to diagnose conditions like asthma and COPD.
4. "Electrocardiogram (ECG)": An ECG records the heart's electrical activity and can identify arrhythmias or signs of heart strain.
5. "Blood Tests": Blood tests can assess oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, as well as markers for heart failure or infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience severe breathing difficulties, especially if accompanied by chest pain, fainting, or confusion. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between "heart" and "lung" issues is crucial in diagnosing breathing problems. By recognizing symptoms and utilizing appropriate diagnostic methods, healthcare providers can pinpoint the cause and recommend effective treatments. If you or someone you know is struggling with breathing issues, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and peace of mind.