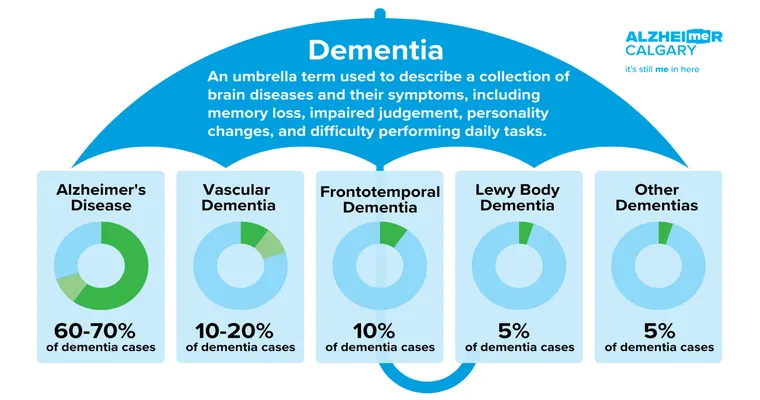
Dementia is a collective term used to describe a variety of brain disorders that lead to a decline in cognitive function, affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities. It is crucial to understand that "different forms of dementia" commonly exhibit "different signs" and symptoms. This diversity in presentation can complicate diagnosis and treatment, making awareness of the unique characteristics of each type vital for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent form of dementia, accounting for approximately 60 to 80 percent of cases. Early signs often include "memory loss", particularly difficulty in remembering newly learned information. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience confusion about time and place, challenges in problem-solving, and changes in mood and personality. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely intervention and support.
Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia is the second most common type and is caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often resulting from strokes or other vascular issues. Symptoms can vary widely but typically include "problems with planning and organizing", difficulty following through on tasks, and a decline in attention span. Individuals may also experience sudden changes in cognitive abilities, which can be linked to specific vascular events.
Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia is characterized by abnormal protein deposits in the brain known as Lewy bodies. Common signs include fluctuations in "alertness and attention", visual hallucinations, and motor symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease. People with this form of dementia may also experience rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder, where they act out their dreams. Understanding these symptoms can help distinguish Lewy body dementia from other types.
Frontotemporal Dementia
Frontotemporal dementia primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to significant changes in personality and behavior. Individuals may display "inappropriate social behavior", a decline in personal hygiene, or a marked lack of empathy. Language difficulties, such as trouble speaking or understanding language, are also common. These behavioral symptoms often appear at a younger age than other types of dementia, typically between the ages of 40 and 65.
Mixed Dementia
Mixed dementia refers to the presence of more than one type of dementia simultaneously, most commonly Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Symptoms can be a combination of both types, making diagnosis particularly challenging. Individuals may experience a range of cognitive declines, including "memory loss", confusion, and changes in behavior, which can complicate treatment options.
Conclusion
Understanding that "different forms of dementia" have "different signs" is essential for early detection and appropriate care. If you or a loved one are experiencing cognitive changes, it is important to consult a healthcare professional who can provide a comprehensive evaluation. Early diagnosis not only aids in managing symptoms but also allows for planning and support tailored to the specific type of dementia, ensuring a better quality of life for all affected.