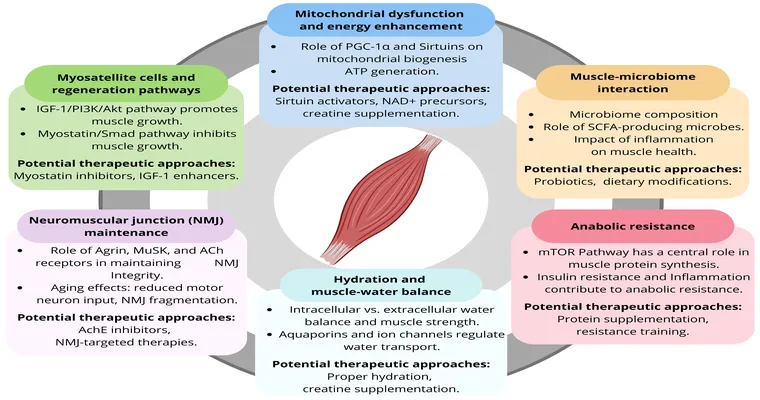
As we age, "sarcopenia" emerges as a significant health concern, characterized by the "loss of muscle mass" and strength. This condition contributes to "frailty", a state that increases the risk of falls, disability, and even mortality among older adults. Understanding people's experiences with sarcopenia is crucial for raising awareness and promoting effective strategies for prevention and management.
Many older adults report a gradual decline in "physical strength" that affects their daily activities. These experiences often begin with subtle signs, such as feeling more fatigued after routine tasks or struggling to lift objects that were once manageable. As sarcopenia progresses, individuals may find themselves unable to participate in social activities, leading to "isolation" and a decrease in overall quality of life.
One common experience shared by those dealing with sarcopenia is the frustration of losing independence. Tasks like climbing stairs, carrying groceries, or even standing up from a chair can become daunting challenges. This decline in muscle strength not only affects physical abilities but can also impact mental health, as feelings of helplessness and anxiety about one’s health become prevalent.
Moreover, many individuals express concern about the lack of awareness surrounding sarcopenia. While some people may associate aging with a natural decline in physical capabilities, they might not realize that targeted interventions can mitigate muscle loss. This realization often leads to a search for solutions, prompting conversations about "nutrition", exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Nutrition plays a vital role in managing sarcopenia. Individuals often recount their efforts to improve their diets, focusing on "protein intake" and consuming foods rich in essential nutrients. High-quality protein sources, such as lean meats, fish, dairy, and legumes, become staples in their meals. Additionally, many adults find that incorporating supplements, such as vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, can support muscle health.
Exercise, particularly "strength training", is another critical aspect of combating sarcopenia. Those who have embraced resistance training report improved muscle mass and overall vitality. They often share stories about how incorporating regular workouts into their routines not only enhances physical strength but also boosts their confidence and mood. Group exercise programs can also foster social connections, reducing feelings of isolation that often accompany frailty.
On the other hand, some individuals struggle to initiate or maintain an exercise regimen due to physical limitations or lack of motivation. This highlights the importance of community resources and support networks that can encourage older adults to stay active. Many express appreciation for local fitness classes specifically designed for seniors, where they can engage with others facing similar challenges.
In summary, the experiences of those coping with "sarcopenia" reveal a complex interplay between physical decline, emotional well-being, and social connections. As awareness grows, it is essential to emphasize the importance of "prevention" and "intervention" strategies to combat the effects of aging on muscle health. By sharing their stories and advocating for better understanding and support, individuals can contribute to a broader conversation about combating frailty and promoting healthier aging.