In recent years, numerous studies have highlighted a concerning connection between "gum disease" and "dementia". As we delve into this topic, it becomes increasingly clear that maintaining good oral health is not just vital for your teeth and gums but may also play a crucial role in protecting your cognitive function as you age. The relationship between these two health issues is multifaceted, prompting researchers and healthcare professionals alike to explore the implications of oral hygiene on overall brain health.
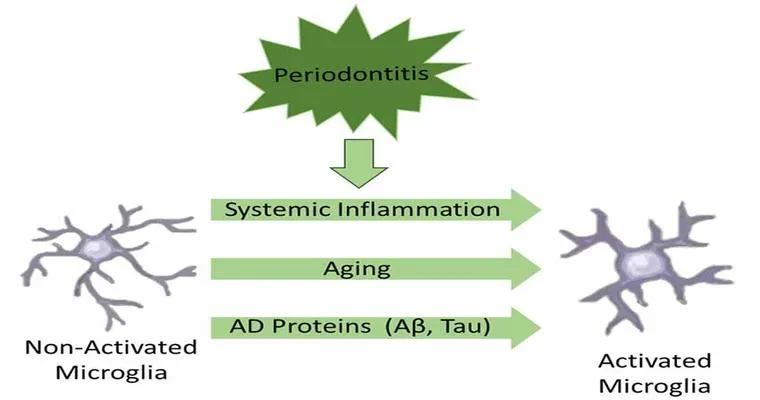
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an inflammatory condition affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is caused primarily by the accumulation of plaque, leading to inflammation, bleeding, and potential tooth loss if left untreated. The bacteria present in gum disease can enter the bloodstream, potentially affecting various organs, including the brain. This is where the connection to dementia becomes particularly intriguing.
Several studies suggest that the bacteria associated with gum disease, such as "Porphyromonas gingivalis", may have a direct impact on brain health. These bacteria can trigger inflammatory responses that may contribute to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. Inflammation is a well-known factor in the progression of dementia, and the presence of harmful bacteria in the mouth could exacerbate this issue.
Moreover, individuals suffering from gum disease may experience a decline in their overall health, which can indirectly influence their cognitive function. Poor oral health can lead to nutritional deficiencies, chronic inflammation, and other systemic health problems, all of which may further increase the risk of developing dementia.
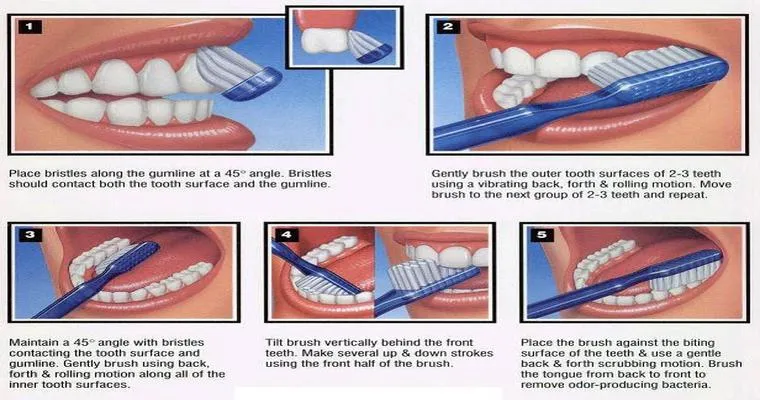
Preventive measures are essential in combating the risks associated with gum disease and its potential link to dementia. Regular dental check-ups, proper brushing and flossing techniques, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can significantly reduce the likelihood of gum disease. Additionally, staying informed about the latest research on "oral health" and its impact on overall well-being is crucial for anyone concerned about cognitive decline.
In conclusion, the articles discussing the relationship between "gum disease" and "dementia" serve as a vital reminder of the importance of oral hygiene. By taking proactive steps to maintain healthy gums, individuals can not only protect their teeth but potentially safeguard their cognitive health as well. As research continues to evolve, staying educated and aware of these connections is essential for promoting a healthier future.