High cholesterol in the elderly is a significant health concern that requires careful attention and management. As people age, their bodies undergo various changes that can lead to increased cholesterol levels. Understanding the implications of "high cholesterol", its "causes", "risk factors", and effective "management strategies" is crucial for promoting cardiovascular health in older adults.
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the blood, essential for building cells and producing certain hormones. However, when cholesterol levels become too high, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, it can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease and stroke. In older adults, high cholesterol often goes hand in hand with other age-related conditions, making it vital to address it promptly.
Several factors contribute to "high cholesterol levels" in the elderly. One major factor is diet. Many older adults may consume diets high in saturated fats and trans fats, which can raise LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle, common among the elderly, can further exacerbate cholesterol issues. Other contributing factors include genetics, comorbidities such as diabetes, and the use of certain medications that can affect cholesterol metabolism.
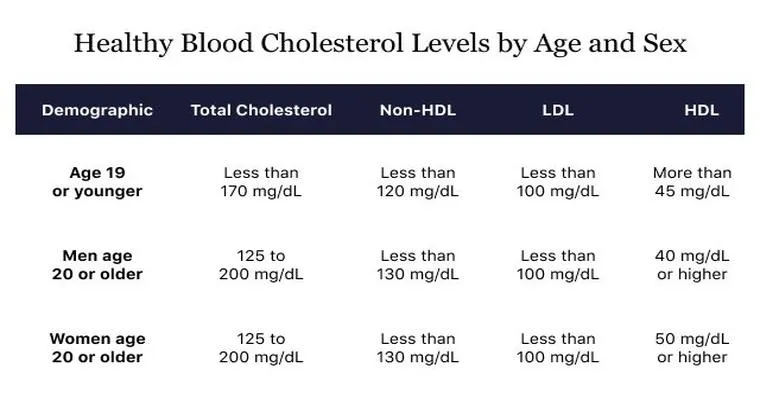
Monitoring cholesterol levels is essential for the elderly. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify those at risk for "high cholesterol". Blood tests can measure total cholesterol, LDL, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglycerides. Understanding these levels can guide necessary lifestyle changes or treatments.
Managing high cholesterol in older adults often involves lifestyle modifications. A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can significantly lower cholesterol levels. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, and those containing soluble fiber, like oats and beans, can also be beneficial. Regular physical activity is another vital component; even moderate exercises like walking can help improve cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to control high cholesterol. Healthcare providers may recommend medications, such as statins, to help lower cholesterol levels effectively. It's crucial for elderly patients to discuss the potential benefits and side effects of these medications with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of action.
In conclusion, high cholesterol in the elderly is a critical health issue that requires a proactive approach. By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with high cholesterol, older adults and their caregivers can take necessary steps to manage their cholesterol levels effectively. Through a combination of dietary changes, regular exercise, and, when needed, medication, it is possible to maintain healthy cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are vital to ensuring the best outcomes for the elderly population.