Colon cancer is a significant health concern, and understanding how it is "diagnosed" and "treated" is crucial for early intervention and effective management. This article will explore the various diagnostic methods used to detect colon cancer and the treatment options available to patients.
Diagnosis of Colon Cancer
The "diagnosis" of colon cancer typically begins with a thorough evaluation of the patient's medical history and a physical examination. Doctors often recommend several diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of colon cancer or to rule out other conditions. The most common methods include:
1. "Colonoscopy": This is the gold standard for diagnosing colon cancer. During a colonoscopy, a flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the rectum to examine the entire colon. If any abnormal growths or polyps are found, they can be biopsied for further analysis.
2. "CT Colonography": Also known as virtual colonoscopy, this imaging test uses CT scans to create detailed images of the colon. It is a less invasive alternative to a traditional colonoscopy and can help identify abnormalities.
3. "Fecal Tests": Stool tests, such as the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and the multi-target stool DNA test, can detect hidden blood or genetic markers associated with colon cancer. These tests are often used for screening purposes.
4. "Biopsy": If colon cancer is suspected, a biopsy is performed during a colonoscopy to remove a small sample of tissue. This sample is then examined under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present.
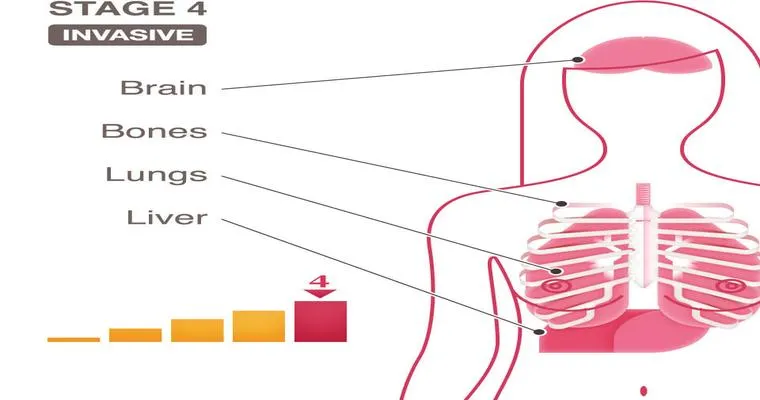
5. "Imaging Tests": In cases where colon cancer is confirmed, additional imaging tests like CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans may be used to determine the extent of the disease and whether it has spread to other organs.
Treatment of Colon Cancer
Once colon cancer is diagnosed, the treatment plan will depend on the stage of the cancer, the location of the tumor, and the overall health of the patient. The main treatment options include:
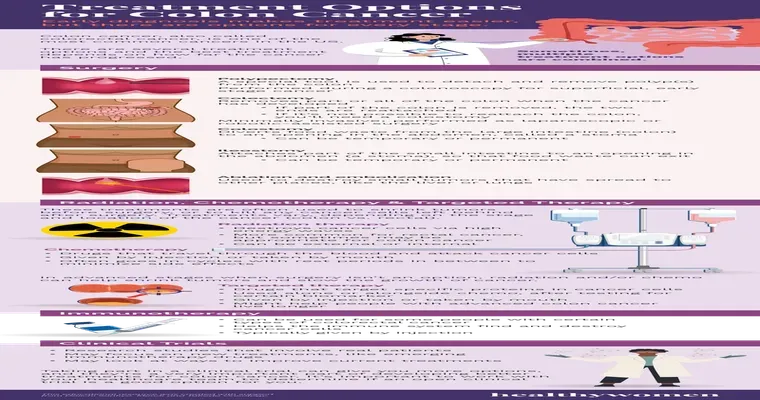
1. "Surgery": Surgical intervention is the most common treatment for colon cancer. The goal is to remove the tumor and any surrounding tissue that may be affected. Depending on the stage of cancer, this may involve removing a portion of the colon (colectomy) or the entire colon (total colectomy).
2. "Chemotherapy": This treatment uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. Chemotherapy may be recommended before surgery to shrink tumors or after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. It can be administered orally or intravenously.
3. "Radiation Therapy": Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It is often used in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy, particularly for rectal cancer or to reduce the size of tumors before surgery.
4. "Targeted Therapy": This innovative treatment focuses on specific characteristics of cancer cells. Targeted therapies may be used for advanced colon cancer and can help inhibit the growth of cancerous cells.
5. "Immunotherapy": For some patients with advanced colon cancer, immunotherapy may be an option. This treatment helps to enhance the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
Conclusion
Early "diagnosis" and prompt "treatment" are vital for improving outcomes in colon cancer patients. Regular screenings and awareness of the symptoms can lead to timely intervention. If you or someone you know is at risk for colon cancer, consult a healthcare professional to discuss appropriate screening methods and treatment options. Remember, early detection saves lives.