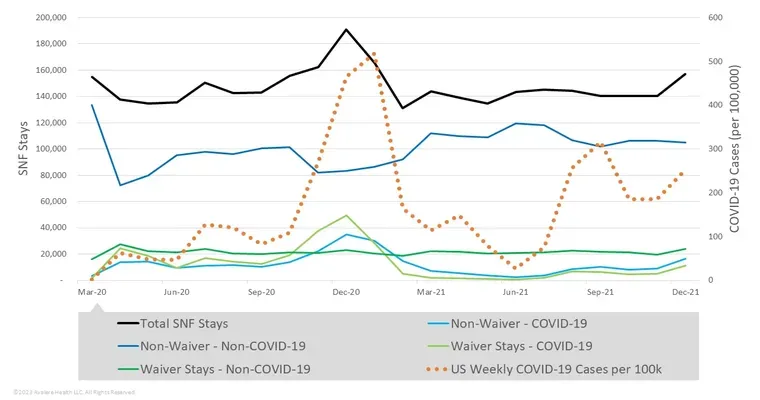
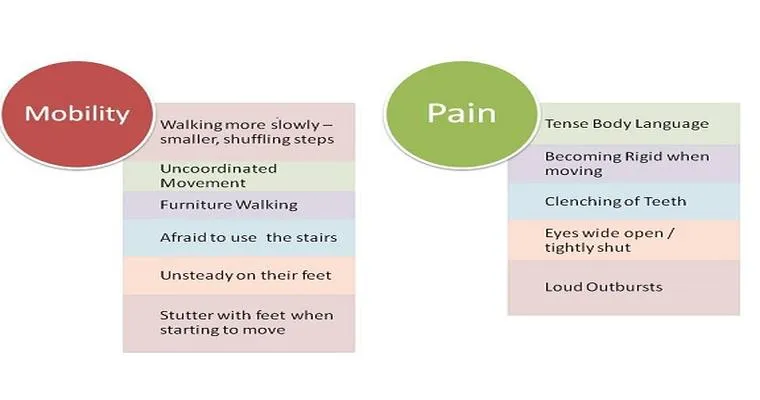
The "sudden decline in Skilled Nursing Facility Managed Care (SNF MC)" is an issue that has garnered attention in recent years. Understanding how common this phenomenon is can help patients, families, and healthcare providers better navigate the complexities of "long-term care" and "healthcare management". This article delves into the prevalence of sudden declines in SNF MC, the factors that contribute to these declines, and what can be done to address them.
Understanding Sudden Decline in SNF MC
Sudden declines in SNF MC refer to abrupt changes in a patient's health status that can lead to increased levels of care or even hospitalization. These declines may manifest as a rapid deterioration in physical or mental health, often accompanied by a loss of functional abilities. While some fluctuations in health can be expected due to age or underlying conditions, a sudden decline can be alarming for patients and their families.
Prevalence of Sudden Declines
Research indicates that sudden declines in SNF MC are not uncommon. Studies show that approximately "15 to 20 percent" of residents experience a significant decline during their stay in a skilled nursing facility. Factors contributing to these declines can include medical complications, lack of proper care, and inadequate staffing. Additionally, certain populations, such as those with "dementia" or multiple chronic conditions, may be at a higher risk.
Factors Contributing to Sudden Declines
Several factors can lead to a sudden decline in SNF MC:
1. "Inadequate Staffing": Insufficient staff levels can result in less personalized care, increasing the risk of health deterioration.
2. "Poor Communication": Miscommunication between healthcare providers and families can lead to unaddressed medical needs.
3. "Medical Complications": Conditions like infections, dehydration, or medication side effects can rapidly impact a patient's health.
4. "Environmental Factors": The physical environment of the SNF, including safety and comfort, can influence a resident's overall well-being.
5. "Mental Health": Emotional and psychological factors, such as depression or anxiety, can also contribute to a sudden decline in health.
Addressing Sudden Declines
Preventing sudden declines in SNF MC requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. "Enhanced Staffing Models": Facilities should ensure adequate staffing levels to provide high-quality care and attention to residents.
2. "Regular Health Assessments": Frequent evaluations can help identify potential issues before they escalate into sudden declines.
3. "Family Involvement": Encouraging family members to participate in care planning can improve communication and ensure that a patient's needs are met.
4. "Training for Staff": Ongoing education and training for staff can equip them with the skills necessary to recognize early signs of decline and intervene appropriately.
5. "Holistic Care Approaches": Addressing both physical and mental health needs can lead to better overall outcomes for residents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sudden declines in SNF MC are a significant concern that affects a notable percentage of residents. Understanding the prevalence and contributing factors can empower families and healthcare providers to take actionable steps to mitigate risks. By focusing on enhanced care strategies and fostering open communication, we can work towards reducing the occurrence of sudden declines and improving the quality of life for those in skilled nursing facilities.