When dealing with a "C. diff infection", many patients and their families wonder about the "customary practices" surrounding discharge from the hospital and the use of "antibiotics at home". Clostridium difficile, commonly known as C. diff, is a bacterium that can cause severe diarrhea and more serious intestinal conditions. Understanding the protocols for discharge and home care is crucial for recovery and preventing further complications.
C. diff infections are often treated in a hospital setting, especially when symptoms are severe. Once stabilized, healthcare providers may consider discharging patients, but there are specific factors that influence this decision. The primary consideration is whether the patient shows signs of improvement and can manage their symptoms at home. Healthcare providers typically assess the severity of the infection, the patient’s overall health, and their ability to follow treatment protocols.
Upon discharge, it is not uncommon for patients to be prescribed "antibiotics" to continue their treatment at home. Antibiotics are essential in combating the infection, but they can also lead to the recurrence of C. diff if not managed properly. Therefore, healthcare professionals often provide detailed instructions on how to take these medications, the importance of adhering to the prescribed regimen, and signs of potential complications that should prompt a return to the hospital.
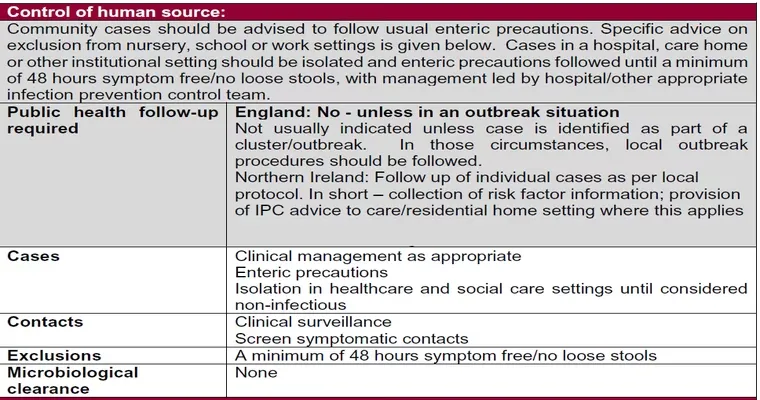
Additionally, patients discharged with a C. diff infection are usually given guidance on dietary modifications and hygiene practices to minimize the risk of spreading the infection to others. This includes thorough handwashing and using separate bathroom facilities when possible. Family members and caregivers are also educated on how to care for the patient and what symptoms to monitor.
It is essential for patients to follow up with their healthcare provider after discharge. Regular check-ins can help ensure that the treatment is effective and that there are no signs of recurrence. If symptoms worsen or new symptoms arise, patients should seek medical attention immediately.
In summary, it is customary for patients with a C. diff infection to be discharged and continue taking antibiotics at home, provided they meet specific health criteria. Close communication with healthcare professionals, adherence to treatment plans, and proactive monitoring are vital components of a successful recovery. Understanding these processes can empower patients and their families to manage C. diff infections effectively and safely at home.