Navigating "Medicare" can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to understanding its "benefits" and "gaps". With various plans available, it's crucial to identify what each offers to choose the best option for your healthcare needs. This article will guide you through the essential components of Medicare, highlighting its benefits and the gaps you should be aware of.
Understanding Medicare
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily designed for individuals aged 65 and older, but it also covers certain younger individuals with disabilities or specific diseases. The program consists of different parts, each serving specific healthcare needs.
1. "Medicare Part A": This part covers hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice, and some home health care. Most individuals don’t pay a premium for Part A if they or their spouse paid Medicare taxes for a certain period.
2. "Medicare Part B": This portion covers outpatient care, doctor visits, preventive services, and some medical supplies. Unlike Part A, Part B does require a monthly premium, and it’s essential to enroll during the initial enrollment period to avoid penalties.
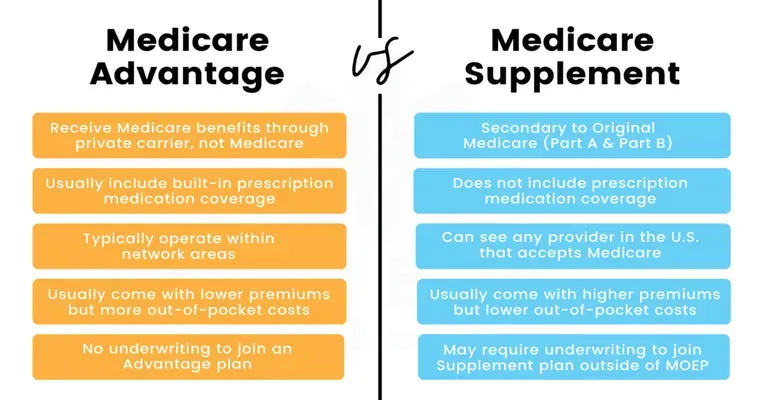
3. "Medicare Part C": Also known as "Medicare Advantage", this plan combines the benefits of Parts A and B and often includes additional coverage like vision, dental, and hearing. These plans are offered by private insurance companies and may have different rules and costs.
4. "Medicare Part D": This part provides prescription drug coverage. Like Part B, you pay a monthly premium for Part D, and it’s crucial to evaluate the specific medications covered by the plan to ensure your needs are met.
Identifying Medicare Gaps
Despite its extensive coverage, Medicare does have certain gaps that beneficiaries should be aware of. Understanding these gaps can help you make informed decisions when selecting a plan:
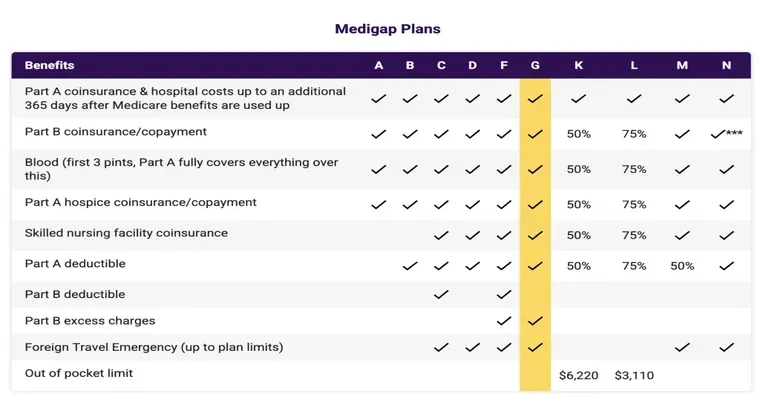
"Cost Sharing": Medicare does not cover all costs. You may be responsible for deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, which can add up quickly, especially during long hospital stays or extensive outpatient treatments.
"Limited Coverage Areas": While Medicare Part A and Part B are accepted at most healthcare facilities, certain specialized services or providers may not accept Medicare, leading to additional out-of-pocket expenses.
"Preventive Services": While many preventive services are covered, some may have restrictions or require specific conditions to be met, which could leave you with unexpected costs.
Choosing the Best Plan
To select the best Medicare plan for your needs, consider the following steps:
1. "Evaluate Your Healthcare Needs": Assess your current health status, medications, and preferred healthcare providers. This information will help you identify which plans cover your specific needs.
2. "Compare Costs": Look at the premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums for each plan. Make sure to account for both monthly payments and potential costs associated with services you may need.
3. "Check Coverage Networks": If you are considering a Medicare Advantage plan, review the provider network to ensure your preferred doctors and hospitals are included.
4. "Review Star Ratings": Medicare assigns star ratings to plans based on quality and performance. These ratings can provide insight into how well a plan meets the needs of its members.
5. "Seek Professional Guidance": If you’re feeling overwhelmed, consider consulting with a Medicare advisor or using online resources. They can help clarify your options and assist you in making the best choice.
Conclusion
Understanding Medicare's "benefits" and "gaps" is essential in selecting the best plan tailored to your healthcare needs. By thoroughly evaluating your options and considering the costs and coverage limitations, you can make an informed decision that ensures you receive the appropriate care without unexpected expenses. Remember, the right plan can significantly impact your overall health and financial well-being in the years to come.