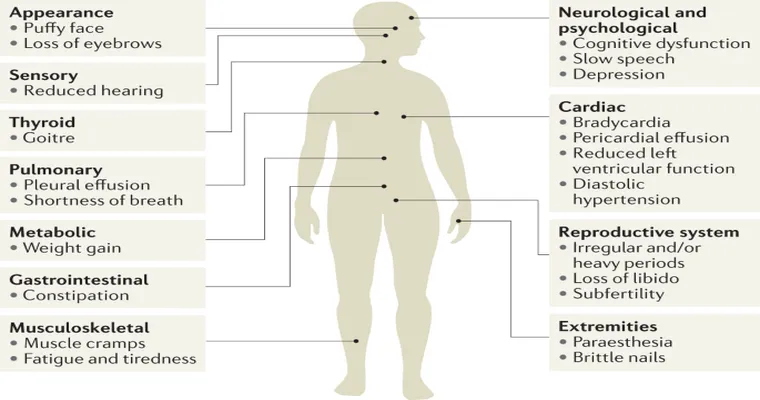
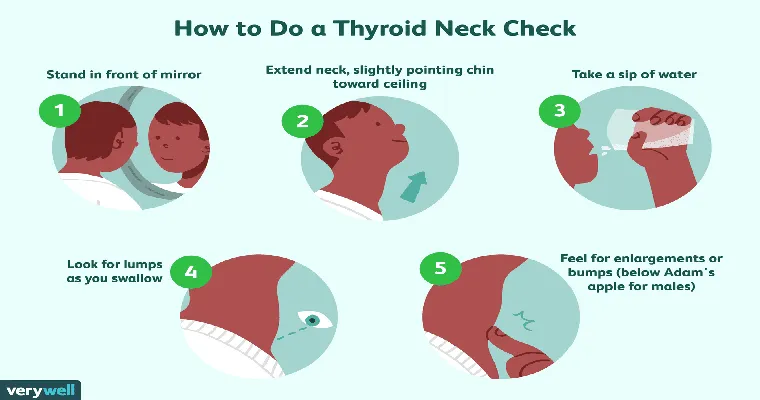
Low thyroid function, commonly known as "hypothyroidism", is a condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall health. When the thyroid fails to produce enough hormones, individuals may experience a range of symptoms including fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold. However, the implications of untreated low thyroid function extend far beyond these initial symptoms, potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
One of the most serious risks associated with untreated "hypothyroidism" is the development of a condition known as "myxedema coma". This rare but life-threatening condition occurs when the body’s metabolic processes slow down to dangerously low levels. Symptoms can include extreme drowsiness, confusion, and even unconsciousness. Myxedema coma requires immediate medical attention, and without prompt treatment, it can result in severe complications or death.
Moreover, low thyroid levels can contribute to cardiovascular problems. Individuals with untreated "hypothyroidism" often experience an increase in cholesterol levels, leading to a higher risk of heart disease. The slowing of metabolic processes can also contribute to high blood pressure, further compounding the risk of heart-related issues. It is essential for individuals with low thyroid function to be monitored regularly to mitigate these dangers.
Another factor to consider is the impact of "hypothyroidism" on mental health. Depression and anxiety are common among those with low thyroid levels. If left untreated, these conditions can escalate, leading to more severe mental health issues, which can significantly impair the quality of life. Addressing low thyroid function can often lead to improvements in mental well-being, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to the effects of untreated "hypothyroidism". Insufficient thyroid hormone levels during pregnancy can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, anemia, and even issues with fetal development. Newborns can suffer from congenital hypothyroidism, which can lead to intellectual disabilities if not detected and treated early. Therefore, monitoring thyroid levels during pregnancy is crucial for the health of both mother and child.
In conclusion, the risks associated with untreated low thyroid function are significant and potentially life-threatening. From the development of myxedema coma to cardiovascular issues and adverse effects on mental health, the ramifications of neglecting this condition can be severe. Regular screening and proactive management of "hypothyroidism" are essential for maintaining health and well-being. If you suspect you have low thyroid function, it is vital to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss appropriate testing and treatment options. Taking action early can make all the difference in preventing serious health complications.