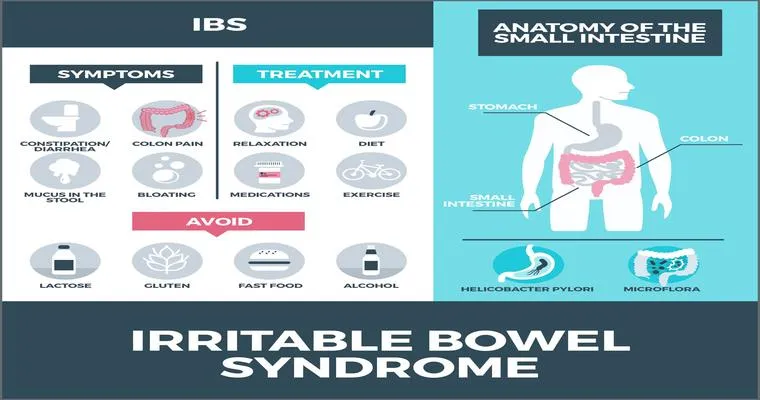
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, commonly referred to as "IBS", is a chronic condition affecting the "gastrointestinal tract". People living with IBS often experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, gas, and "changes in bowel habits", including diarrhea and constipation. Understanding how to manage and cope with IBS can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by this disorder.
Understanding IBS
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder, meaning it involves issues with how the gut functions, rather than structural abnormalities. While the exact cause of IBS is still unclear, factors such as "diet", "stress", and "gut microbiota" are believed to play significant roles in its onset and exacerbation. Recognizing the symptoms and triggers is crucial for effective management.
Identifying Triggers
One of the first steps in managing IBS is identifying personal "triggers". Many individuals find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms. Common culprits include dairy products, spicy foods, caffeine, and high-fat meals. Keeping a "food diary" can help in tracking what you eat and how it affects your symptoms. This practice can provide insights into which foods to avoid and help in developing a more tolerable diet.
Dietary Changes
Implementing dietary changes can greatly ease the symptoms of IBS. The "low FODMAP diet" has gained popularity in recent years as an effective approach for managing IBS symptoms. FODMAPs are certain types of carbohydrates that can be difficult for some individuals to digest. Reducing high FODMAP foods like garlic, onions, and certain fruits can lead to significant symptom relief. Incorporating more soluble fiber from sources such as oats, bananas, and carrots can also help regulate bowel movements.
Stress Management
Stress is another significant factor that can exacerbate IBS symptoms. Learning stress management techniques, such as "mindfulness", "yoga", and "meditation", can be beneficial. Regular physical activity not only helps reduce stress but also promotes overall gut health. Finding time to relax and practice self-care can make a significant difference in managing IBS.
Seeking Professional Help
If you suspect you have IBS or are struggling to manage your symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. A "gastroenterologist" can provide a proper diagnosis and help develop a tailored management plan. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms, including antispasmodics for abdominal pain or laxatives for constipation.
Support Networks
Living with IBS can feel isolating, but connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide valuable support. Many online forums and local support groups cater to individuals with IBS, offering a space to share stories, tips, and coping mechanisms. Engaging with a community can help reduce feelings of anxiety and isolation that often accompany chronic health conditions.
Conclusion
Living with Irritable Bowel Syndrome presents its challenges, but with the right strategies and support, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life. By understanding your triggers, making dietary adjustments, managing stress, and seeking professional help, you can take control of your symptoms. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you navigate the complexities of IBS.