Prostate problems are common among men, especially as they age. Understanding the various "medical tests for prostate problems" is essential for early detection and effective treatment. This article will explore the most common diagnostic procedures used to evaluate prostate health, including the "PSA test", digital rectal exam, and imaging techniques.
One of the primary tests conducted to assess prostate health is the "Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test". This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels can indicate the presence of prostate issues, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, or prostate cancer. It is important to note that while high PSA levels can be a warning sign, they are not definitive proof of cancer, making further testing necessary.
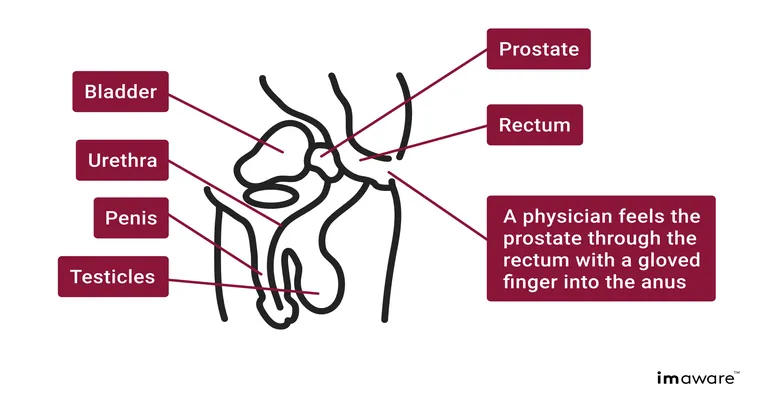
Another crucial procedure is the "digital rectal exam (DRE)". During this exam, a healthcare provider inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland. The DRE helps identify abnormalities in size, shape, or texture that may suggest prostate problems. This exam is often performed alongside the PSA test for a comprehensive evaluation.
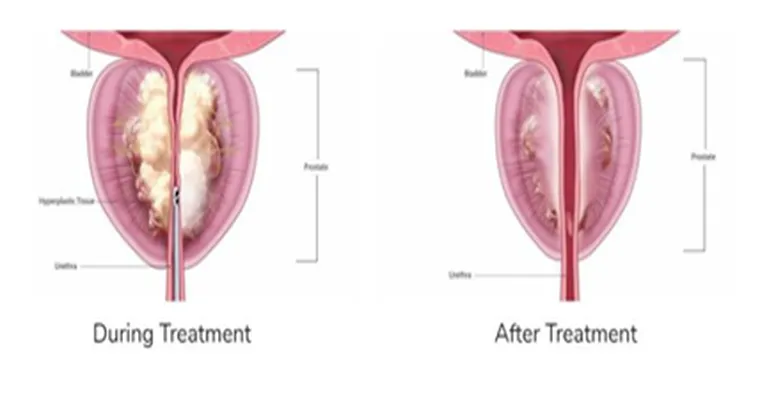
In some cases, if initial tests suggest a potential issue, a "biopsy" may be required. A biopsy involves taking small samples of prostate tissue to examine them for cancer cells. This procedure is typically guided by imaging techniques, such as "transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)", which helps the doctor visualize the prostate and ensure accurate sampling.
Imaging tests, such as "MRI" or "CT scans", can also be used to evaluate prostate problems. These advanced imaging techniques provide detailed images of the prostate and surrounding tissues, helping to determine the extent of any abnormalities. They are particularly useful in staging prostate cancer and planning appropriate treatment.
Regular screenings and awareness of symptoms such as difficulty urinating, painful urination, or blood in urine are essential for early detection of prostate issues. Men over the age of 50, or younger men with a family history of prostate problems, should discuss the need for these "medical tests for prostate problems" with their healthcare provider.
In conclusion, understanding and utilizing the various "medical tests for prostate problems" can significantly impact men's health. Early detection through PSA testing, digital rectal exams, biopsies, and imaging can lead to timely interventions, improving outcomes for those facing prostate-related issues. If you have concerns about your prostate health, consult a healthcare professional to discuss the best testing options for you.