Metastatic prostate cancer is a serious condition where cancer cells spread beyond the prostate gland to other parts of the body. This advanced stage of prostate cancer can significantly affect a patient's health and requires comprehensive treatment strategies. One of the treatment options that may be considered for patients with "metastatic prostate cancer" is "chemotherapy". Understanding the role of chemotherapy in managing this condition can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
What is Metastatic Prostate Cancer?
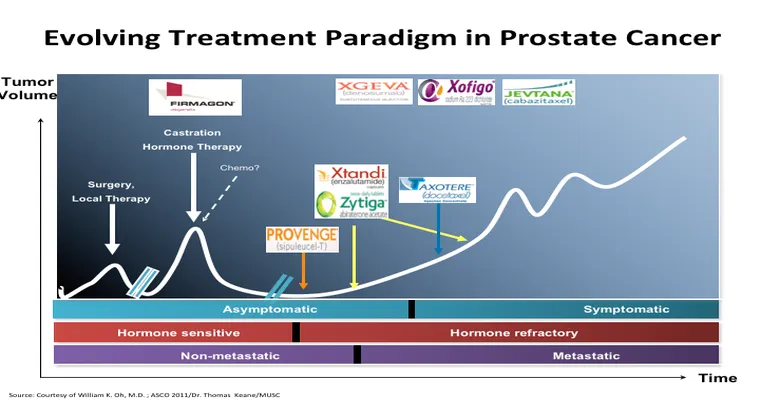
Metastatic prostate cancer occurs when prostate cancer cells migrate from the prostate to other organs, most commonly the bones, lymph nodes, liver, and lungs. Symptoms may include bone pain, fatigue, weight loss, and changes in urinary habits. Early detection and treatment are crucial, but once the cancer has metastasized, the treatment becomes more complex, often requiring a combination of therapies.
The Role of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. In the context of "metastatic prostate cancer", chemotherapy is generally used when the cancer has become resistant to hormone therapy, which is often the first line of treatment. Chemotherapy can help manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and extend survival for some patients.
Common Chemotherapy Drugs
The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for metastatic prostate cancer include "docetaxel" and "cabazitaxel". Docetaxel is often the first choice and is typically administered in combination with prednisone to enhance effectiveness. Cabazitaxel is used for patients whose cancer has progressed despite docetaxel treatment. Both of these drugs can have side effects, including nausea, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection, which need to be monitored by healthcare professionals.
Treatment Protocols
The treatment protocol for metastatic prostate cancer often involves cycles of chemotherapy. Each cycle usually lasts several weeks and includes a period of treatment followed by a rest period to allow the body to recover. The specific regimen may vary based on individual patient factors, such as overall health, prior treatments, and cancer characteristics.
Additional Treatments
While chemotherapy can be an effective option, it is often part of a broader treatment plan. Doctors may recommend additional therapies, such as "hormone therapy", "radiation therapy", or "immunotherapy", depending on the patient's specific condition and response to treatment. Combining these therapies can enhance effectiveness and improve outcomes.
Managing Side Effects
The side effects associated with chemotherapy can vary widely among individuals. It is essential for patients to communicate openly with their healthcare team about any side effects they experience. Supportive care, including medications to manage nausea, pain, and fatigue, can significantly improve the quality of life during treatment.
Conclusion
Metastatic prostate cancer presents significant challenges, but chemotherapy remains a critical component of the treatment arsenal. With advancements in cancer care, many patients can find effective ways to manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life. For those facing this diagnosis, understanding the role of chemotherapy, its potential benefits, and its side effects is vital in making informed decisions about their treatment journey. Always consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best options tailored to individual needs.