Mild or "early dementia" is a stage of cognitive decline that affects an individual's memory, thinking, and social abilities. This condition can significantly impact daily life, making it essential to recognize the "early signs of dementia" and understand how to manage them effectively. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, potential causes, and management strategies for individuals experiencing mild dementia.
Signs and Symptoms of Mild Dementia
The symptoms of mild dementia can vary from person to person, but some common "early signs of dementia" include:
"Memory loss": Individuals may forget recent events or conversations.
"Difficulty with problem-solving": Tasks that once seemed easy may become challenging, such as managing finances or following a recipe.
"Confusion": Affected individuals may become disoriented in familiar places or struggle to keep track of dates and times.
"Changes in mood and personality": Those with mild dementia may experience mood swings, increased anxiety, or noticeable changes in their personality.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and intervention, improving the quality of life for those affected.
Causes of Mild Dementia
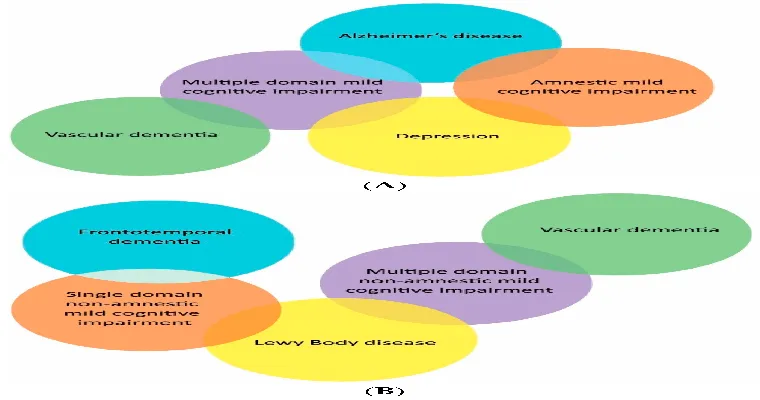
Mild dementia can result from several underlying conditions, including:
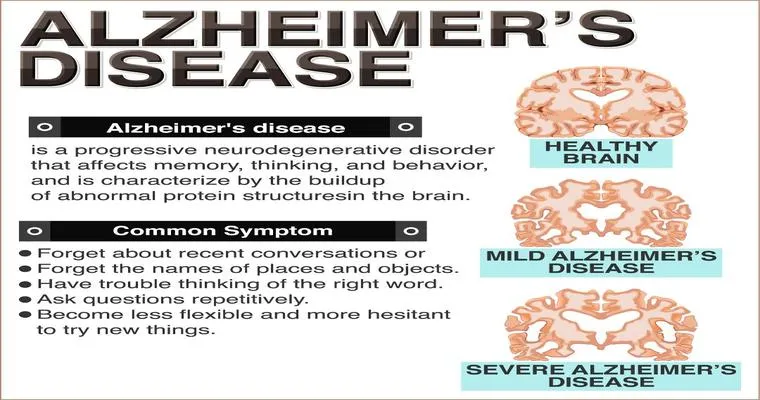
"Alzheimer's disease": The most common cause of dementia, characterized by gradual memory loss and cognitive decline.
"Vascular dementia": Often caused by strokes or other issues that affect blood flow to the brain.
"Lewy body dementia": This type involves abnormal protein deposits in the brain, leading to cognitive fluctuations and visual hallucinations.
"Frontotemporal dementia": Affects the frontal and temporal lobes, leading to changes in personality and behavior.
Understanding the underlying cause of mild dementia is crucial for developing an effective care plan.
Diagnosis and Assessment
If you or a loved one is exhibiting signs of mild dementia, seeking a professional evaluation is essential. A healthcare provider can conduct a comprehensive assessment that may include:
"Medical history": Discussing symptoms, family history, and overall health.
"Cognitive tests": Evaluating memory, problem-solving skills, and other cognitive functions.
"Brain imaging": MRI or CT scans may be used to identify any structural changes in the brain.
An accurate diagnosis can help tailor treatment and management plans.
Management Strategies for Mild Dementia
While there is currently no cure for dementia, various strategies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
"Cognitive therapy": Engaging in activities that stimulate the brain, such as puzzles, reading, or memory games.
"Physical exercise": Regular physical activity can enhance overall well-being and cognitive function.
"Healthy diet": A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is beneficial for brain health.
"Social engagement": Maintaining social connections and participating in community activities can reduce feelings of isolation and depression.
"Medication": In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to help manage symptoms or slow cognitive decline.
Support for Caregivers
Caring for someone with mild dementia can be challenging. It is essential for caregivers to seek support and resources to help manage their responsibilities and maintain their well-being. Support groups, educational resources, and respite care can provide valuable assistance.
Conclusion
Mild or early dementia is a significant health concern that requires attention and care. By recognizing the "early signs of dementia", understanding the potential causes, and implementing effective management strategies, individuals and their families can navigate this challenging journey. Early intervention and support can make a substantial difference in the lives of those affected. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be experiencing symptoms of mild dementia, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support.