When deciding between an "occupational therapy" consult and a "physical therapy" consult, it is essential to understand the distinct roles each discipline plays in rehabilitation and recovery. Both therapies aim to improve a person's quality of life, but they focus on different aspects of health and wellness. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about which professional to consult based on your specific needs.
Understanding Occupational Therapy
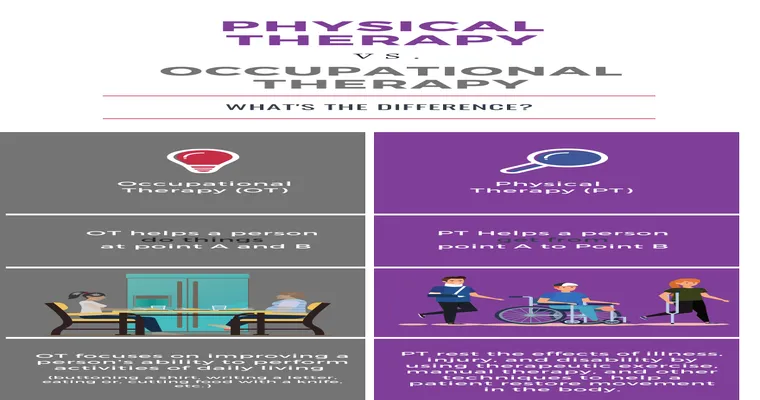
"Occupational therapy" focuses on helping individuals develop, recover, or maintain daily living and work skills. This therapy is particularly beneficial for people who have experienced injuries, disabilities, or illnesses that affect their ability to perform everyday tasks. Occupational therapists assess the patient's needs and create personalized treatment plans that may include exercises, adaptive equipment, and strategies to enhance independence in daily activities.
The Role of Physical Therapy
On the other hand, "physical therapy" primarily targets the physical aspects of recovery. Physical therapists work with patients to improve their physical function and mobility through exercises, manual therapy, and other modalities. This therapy is often recommended for those recovering from surgery, injury, or chronic pain conditions. A physical therapist evaluates the patient's movement patterns and develops a treatment plan aimed at restoring strength, flexibility, and coordination.
Key Differences
The main differences between "occupational therapy" and "physical therapy" lie in their objectives and methodologies. While occupational therapy emphasizes the overall ability to engage in daily activities and work, physical therapy is focused on physical rehabilitation and strengthening. For instance, if you are recovering from a stroke and need help with dressing or cooking, an occupational therapist would be the appropriate choice. Conversely, if you are dealing with a sports injury that affects your mobility, a physical therapist would be more suitable.
When to Choose Occupational Therapy
Consider an "occupational therapy" consult if you are experiencing challenges with:
Daily living activities like bathing, dressing, or cooking
Cognitive challenges that impact your ability to perform tasks
A need for adaptive equipment to enhance your independence
When to Choose Physical Therapy
A "physical therapy" consult might be the best option if you are facing issues such as:
Pain or injury that limits your range of motion
Recovery from surgery related to musculoskeletal issues
A need for rehabilitation after a sports injury
Combining Both Therapies
In some cases, individuals may benefit from both "occupational therapy" and "physical therapy". For example, after a major surgery, a patient might first require physical therapy to regain strength and mobility, followed by occupational therapy to relearn daily activities. Collaborating with both professionals can provide a comprehensive approach to recovery.
Conclusion
Choosing between an "occupational therapy" or "physical therapy" consult ultimately depends on your specific needs and goals. Understanding the unique focus of each therapy can guide you in making the right decision. If you are still uncertain, consider consulting with your healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms and get recommendations tailored to your situation. By making an informed choice, you can take significant steps toward recovery and improved quality of life.