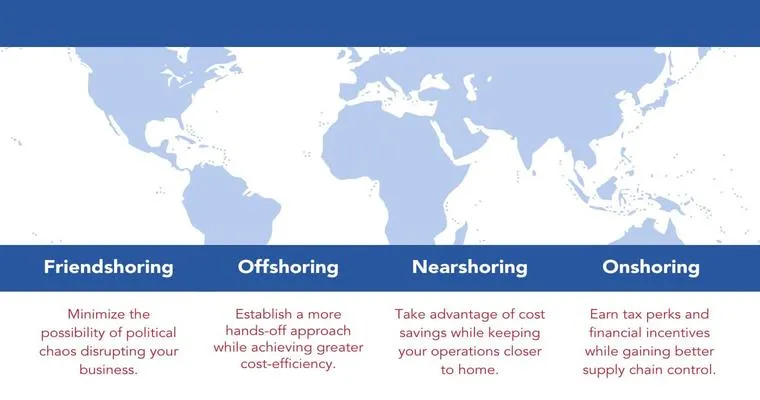
In today's global economy, "outsourcing", "onshore sourcing", "near sourcing", "off sourcing", and "multi sourcing" have become buzzwords that define how businesses operate. These strategies aim to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance service delivery. However, as companies chase "cheap labor" and operational savings, the question arises: who's really hurt by these decisions?
Understanding the Concepts
"Outsourcing" refers to the practice of hiring third-party organizations to handle business functions that were previously done in-house. This can involve everything from manufacturing to customer service. "Onshore sourcing" is when companies source services or products from within their own country, while "near sourcing" brings services closer to home but may involve neighboring countries. In contrast, "off sourcing" typically involves moving jobs to countries with lower labor costs. Lastly, "multi sourcing" is a strategy that involves using multiple vendors for a single project or service, thereby diversifying risk and optimizing costs.
The Appeal of Cheap Labor
Businesses are often drawn to "cheap labor" markets, leading to significant cost savings. These savings can be reinvested into the company, leading to growth and potentially more jobs. However, while companies may benefit financially, the consequences can ripple through the economy and society.
Economic Impact
The shift towards "outsourcing" and "off sourcing" has led to job losses in many developed countries. Skilled workers find themselves competing with a global workforce willing to accept lower wages. This can lead to a decline in job security, resulting in a workforce that is increasingly anxious and less loyal to their employers.
Quality and Service Concerns
While cost is a major factor, the quality of services can suffer when businesses prioritize "cheap" solutions. For instance, "outsourcing" customer service to countries where language barriers exist can result in poor customer experiences, ultimately harming brand reputation. Similarly, manufacturing processes may compromise quality control when oversight is reduced in favor of cost savings.
The Human Cost
The social implications of these sourcing strategies are profound. Families are affected when breadwinners lose their jobs, leading to increased financial strain and emotional distress. Communities can suffer as local businesses decline when larger companies choose "off sourcing" options.
Balance and Responsibility
To mitigate the negative impacts of these strategies, companies should strive for a balance between cost savings and social responsibility. Embracing "onshore sourcing" or "near sourcing" can create local jobs and boost the economy, while still maintaining cost-effectiveness. "Multi sourcing" can also provide a safety net, reducing reliance on any single vendor and encouraging competitive pricing without sacrificing quality.
Conclusion
While "outsourcing", "near sourcing", "off sourcing", and "multi sourcing" present opportunities for businesses to minimize costs, the repercussions can be significant. The impact on local economies, job security, and service quality cannot be ignored. Companies must weigh the benefits of "cheap labor" against the potential harm to their workforce and communities. By fostering a responsible sourcing strategy, businesses can contribute to a healthier economy while still enjoying the advantages of cost-effective solutions.