"Radiation therapy" is a crucial treatment option in the fight against cancer. This medical procedure utilizes high doses of "radiation" to target and kill cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. It is frequently employed as a primary treatment for various types of cancer or as an adjunct to other treatments such as "surgery" and "chemotherapy". Understanding how radiation therapy works, its benefits, and potential side effects is essential for patients and their families navigating the complexities of cancer treatment.
How Radiation Therapy Works
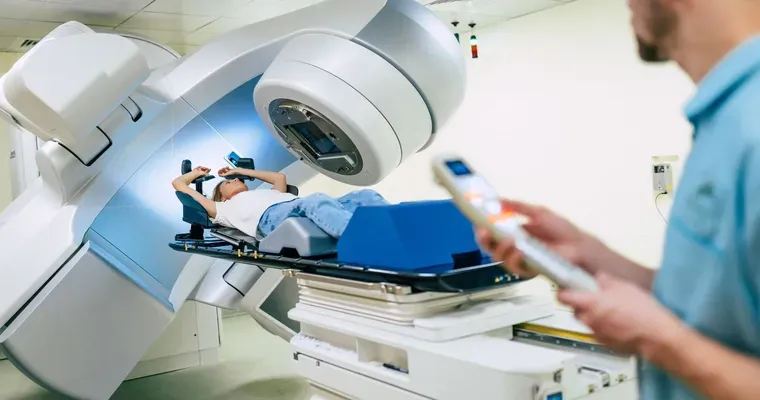
Radiation therapy aims to destroy the DNA of cancer cells, rendering them unable to grow and divide. The treatment can be delivered in two primary forms: "external beam radiation therapy (EBRT)" and "internal radiation therapy" (also known as brachytherapy). EBRT involves directing high-energy beams from outside the body to the tumor, while internal radiation involves placing a radioactive source directly inside or near the tumor.
Types of Radiation Therapy
There are several types of radiation therapy used in cancer treatment:
1. "External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)": This is the most common form, where radiation is delivered from a machine called a linear accelerator. It is often used for tumors that are localized and can be targeted precisely.
2. "Brachytherapy": This involves placing radioactive material inside or near the tumor. It is commonly used for cancers of the prostate, cervix, and breast.
3. "Stereotactic Radiosurgery": This non-invasive procedure delivers precise, high doses of radiation to tumors in the brain or other areas while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue.
4. "Systemic Radiation Therapy": This method involves administering radioactive substances through the bloodstream, targeting cancer cells throughout the body. It is often used for thyroid cancer and certain types of lymphoma.
Benefits of Radiation Therapy
One of the primary advantages of radiation therapy is its ability to target tumors effectively while preserving healthy cells. Some benefits include:
"Localized Treatment": Radiation can be focused on specific areas, making it an effective option for localized cancers.
"Pain Relief": For cancers that have spread to bones or other parts of the body, radiation can help alleviate pain and improve quality of life.
"Shrink Tumors": Prior to surgery, radiation may be used to shrink tumors, making them easier to remove.
Side Effects of Radiation Therapy
While radiation therapy can be highly effective, it is not without potential side effects. Common side effects include:
"Fatigue": Many patients experience a general sense of tiredness during and after treatment.
"Skin Changes": The skin in the treated area may become red, irritated, or sensitive.
"Nausea": Some patients may experience nausea, particularly if the abdomen is treated.
"Long-term Effects": In some cases, patients may face long-term effects such as changes in skin texture or secondary cancers.
Conclusion
Radiation therapy is a vital component of modern cancer treatment, offering patients a targeted approach to combating various types of cancer. Understanding the types, benefits, and potential side effects can empower patients and their families to make informed decisions about their treatment options. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to discuss the best approach tailored to individual needs. As research and technology continue to advance, radiation therapy remains a cornerstone in the ongoing battle against cancer, providing hope and improved outcomes for countless patients.