Dementia often brings about a range of challenges, including "anxiety" that can significantly impact the quality of life for both patients and caregivers. When seeking "medications" to help manage anxiety associated with dementia, patients may encounter specific limitations, particularly if they are on "blood pressure medication". Understanding the options available and the considerations involved can help guide discussions with healthcare professionals.
Understanding Anxiety in Dementia
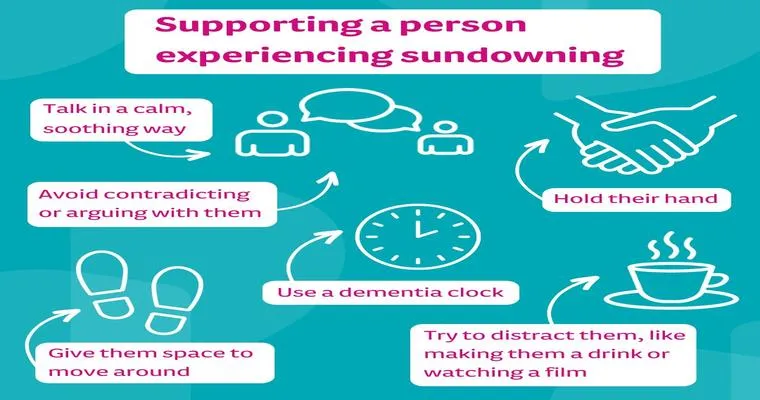
Anxiety is a common symptom in individuals with dementia, manifesting as restlessness, agitation, or excessive worry. It can stem from confusion, changes in routine, or even fear of the unknown. The interplay between dementia and anxiety can complicate treatment, especially when other health conditions like high blood pressure are present.
Medication Options for Managing Anxiety
While there are several "medications" that can alleviate anxiety, not all are suitable for individuals with dementia who are also taking blood pressure medications. Here are some potential options that may be considered:
1. "SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors)": Medications like sertraline or escitalopram are often prescribed for anxiety and depression. They can be effective for some dementia patients, but monitoring is essential due to potential interactions with blood pressure medications.
2. "Buspirone": This is an anxiolytic that is less likely to cause sedation and may be suitable for patients who have anxiety without significant sedation risks. It is also generally well-tolerated when managed alongside blood pressure drugs.
3. "Non-Pharmacological Interventions": Before turning to medications, consider therapies like "cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)", mindfulness practices, and relaxation techniques. These approaches can provide significant relief without the risks associated with pharmacotherapy.
4. "Low-Dose Antipsychotics": In some cases, low doses of atypical antipsychotics like quetiapine may be used cautiously to manage severe anxiety symptoms. However, these should be carefully considered due to potential side effects and interactions.
Communication with Healthcare Providers
If you or a loved one is dealing with dementia-related anxiety and are on blood pressure medication, it is crucial to have open discussions with healthcare providers. Be clear about the anxiety symptoms being experienced and inquire about any alternative treatments that may not interfere with existing medications.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, consider integrating lifestyle modifications to reduce anxiety levels. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and maintaining a consistent routine can help ease anxiety symptoms. Engaging in social activities or hobbies can also provide distraction and a sense of normalcy.
Conclusion
Managing "dementia anxiety" can be challenging, especially when blood pressure medications limit the options available. By working closely with healthcare providers, exploring various treatment pathways, and considering lifestyle changes, individuals can find effective ways to alleviate anxiety and improve their overall well-being. Remember, it’s vital to tailor any treatment approach to the individual’s unique health profile and needs.