As we age, the risk of developing "blood clots" increases significantly, particularly in seniors. Understanding the "symptoms" of blood clots is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can prevent serious complications. Blood clots can occur in various parts of the body, with the most common types being "deep vein thrombosis (DVT)" and "pulmonary embolism (PE)". This article will explore the key symptoms that seniors should be aware of to identify potential blood clots early.
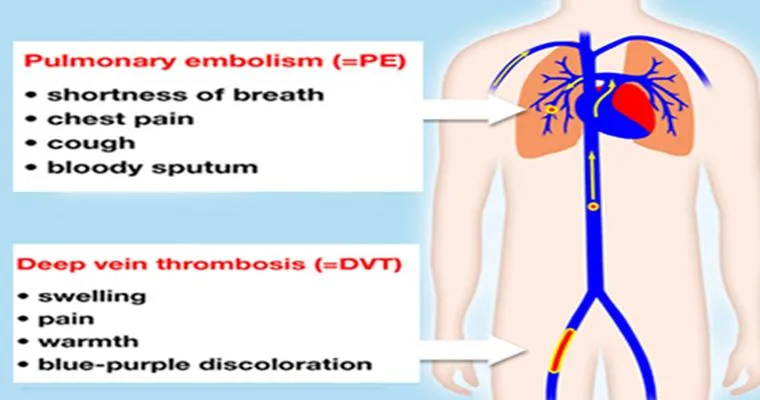
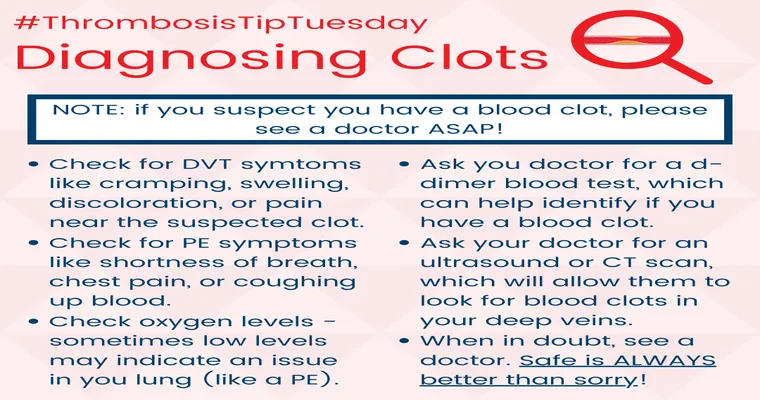
One of the hallmark symptoms of "deep vein thrombosis" is swelling in one leg, often accompanied by pain or tenderness. Seniors may notice that one leg appears larger than the other or feels warmer to the touch. This swelling typically occurs in the calf or thigh and may be mistaken for other conditions like arthritis or a muscle strain. It is imperative for seniors to pay close attention to these changes and seek medical advice if they experience such symptoms.
In addition to swelling, another common symptom of a blood clot is a sudden onset of pain. This pain can feel like cramping or soreness and may worsen with movement. It's crucial for seniors to differentiate between regular muscle pain and potential signs of a blood clot. If the pain is persistent and localized to one leg, it should not be ignored.
"Pulmonary embolism" presents different symptoms and can occur if a blood clot travels to the lungs. Seniors may experience shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, or chest pain that may worsen with deep breaths. These symptoms can be mistaken for other respiratory issues, making it essential for seniors to report any sudden changes in their breathing patterns to their healthcare provider.
In some cases, seniors may also experience symptoms that are less commonly associated with blood clots but are nonetheless significant. These include lightheadedness or dizziness, coughing up blood, and a feeling of anxiety or impending doom. While these symptoms can be caused by various conditions, they should prompt immediate medical attention, especially when occurring alongside other symptoms of blood clots.
Prevention is key when it comes to blood clots, particularly for seniors who may be at higher risk due to factors such as immobility, surgery, or certain medical conditions. Staying active, maintaining hydration, and wearing compression stockings can all help reduce the risk of developing blood clots.
In conclusion, being aware of the "symptoms" of blood clots is vital for seniors. Recognizing signs such as swelling, pain, and shortness of breath can lead to timely medical intervention and potentially save lives. Seniors and their caregivers should remain vigilant and consult healthcare professionals if they notice any concerning symptoms. Early detection and treatment are essential in managing the risks associated with blood clots effectively.