Sepsis is a "life-threatening condition" that arises when the body's response to an infection spirals out of control. It is one of the leading causes of "preventable death", yet many people remain unaware of its severity and prevalence. Understanding sepsis, its symptoms, and the importance of early intervention can be crucial in saving lives.
What is Sepsis?
Sepsis occurs when an infection triggers a chain reaction throughout the body. It can be caused by various infections, including those of the lungs, urinary tract, abdomen, and skin. The body's immune response becomes dysregulated, leading to "inflammation", tissue damage, and, in severe cases, "organ failure". The condition can escalate rapidly, making early recognition and treatment vital.
Symptoms of Sepsis
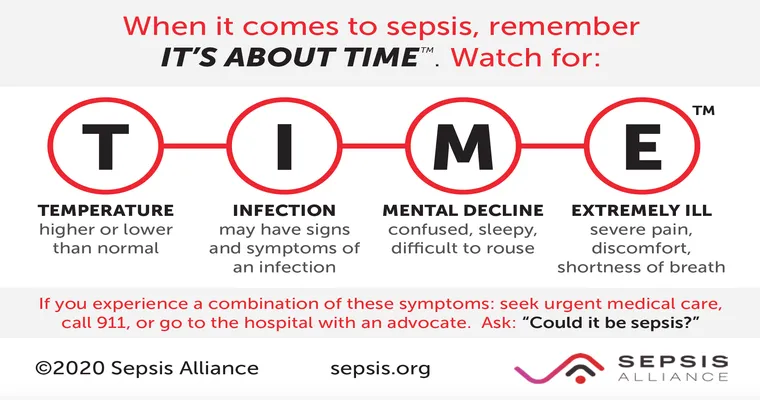
Recognizing the symptoms of sepsis is essential for timely medical intervention. Early signs may include:
Fever or low body temperature
Increased heart rate
Rapid breathing
Confusion or disorientation
As the condition worsens, symptoms can escalate to include severe "fatigue", difficulty breathing, and a significant drop in blood pressure, leading to septic shock. If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Who is at Risk?
While anyone can develop sepsis, certain populations are at a higher risk. This includes:
Individuals with weakened immune systems
Elderly adults
Infants and young children
People with chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes or liver disease
Understanding your risk factors can help in taking preventive measures and recognizing the early signs of sepsis.
The Importance of Early Detection
The key to surviving sepsis lies in early detection and treatment. The longer sepsis goes untreated, the higher the risk of severe complications. Medical professionals often use the "Sepsis Six" approach, which involves:
1. Administering oxygen
2. Taking blood cultures
3. Administering intravenous antibiotics
4. Administering intravenous fluids
5. Monitoring vital signs
6. Assessing the need for additional interventions
Quick action can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the likelihood of long-term health issues or death.
Preventing Sepsis
Preventing sepsis begins with proper hygiene and health practices, such as:
Getting vaccinated to prevent infections
Practicing good hand hygiene
Taking care of wounds and cuts promptly
Managing chronic conditions effectively
Education about sepsis and its risks can empower individuals to take proactive steps in their health care, potentially saving lives.
Conclusion
Sepsis is a "silent killer" that claims millions of lives each year, often without warning. Raising awareness about the symptoms, risks, and the importance of early treatment can help combat this "common cause of death". By understanding sepsis, we can reduce its incidence and improve outcomes for those affected. If you suspect sepsis, do not hesitate to seek immediate medical assistance. Knowledge is the first step in the fight against this critical health issue.