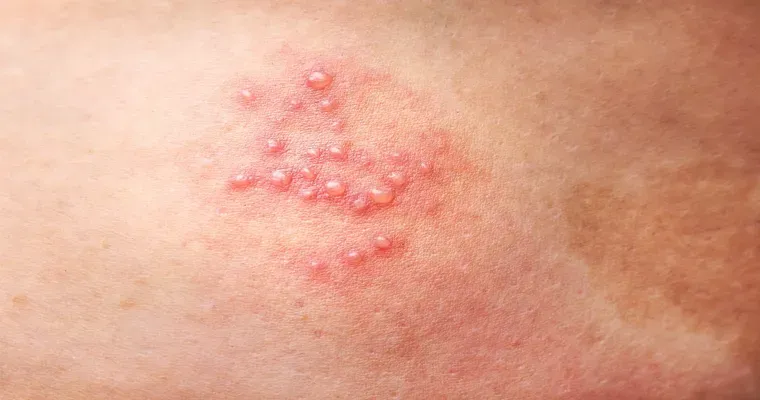
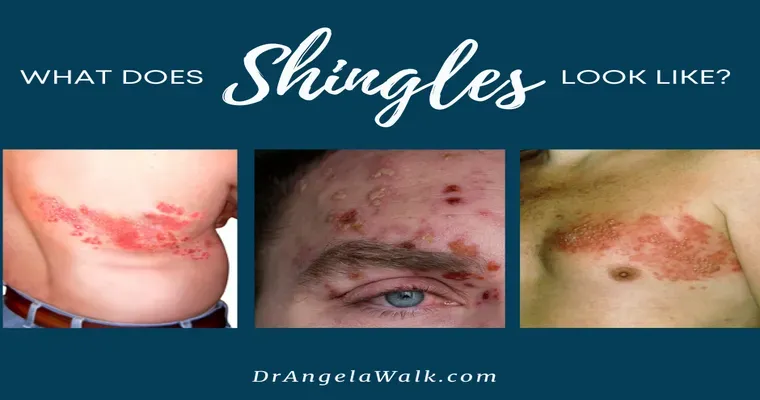
Shingles, also known as "herpes zoster", is a painful skin condition that results from the reactivation of the "varicella-zoster virus", the same virus that causes chickenpox. This condition primarily affects adults and can lead to severe discomfort, characterized by a painful "rash" and "blisters". Understanding shingles is crucial for early identification and treatment, as well as for preventing complications associated with this condition.
What Causes Shingles?
After a person has chickenpox, the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the nervous system. Years later, this virus can reactivate, leading to shingles. While the exact reason for this reactivation is not fully understood, it is often associated with a weakened "immune system", stress, or certain medications. Individuals aged 50 and above are particularly at risk, as well as those with conditions that compromise the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or cancer.
Symptoms of Shingles
The symptoms of shingles typically begin with a tingling or burning sensation on one side of the body, usually accompanied by fatigue and fever. Within a few days, a "rash" develops, forming clusters of painful "blisters" that can break open and crust over. The rash usually appears in a band-like pattern, following the path of affected nerves. The pain associated with shingles can be intense and is often described as sharp, stabbing, or a deep ache. This pain may persist even after the rash has healed, a condition known as "postherpetic neuralgia".
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have shingles, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Diagnosis is usually based on the appearance of the rash and the patient’s medical history. Early treatment is essential in managing the symptoms and can significantly reduce the duration of the outbreak.
Antiviral medications, such as "acyclovir", "valacyclovir", or "famciclovir", are commonly prescribed to help speed up recovery and lessen the severity of symptoms. Additionally, pain relievers, topical creams, and corticosteroids may be recommended to alleviate discomfort. It is important to start treatment as soon as possible, ideally within 72 hours of the onset of the rash.
Prevention of Shingles
Preventing shingles primarily involves boosting the immune system. The "shingles vaccine", known as "Shingrix", is highly recommended for adults over 50 and those at higher risk of developing shingles. This vaccine can significantly reduce the chances of contracting shingles and can also lower the risk of postherpetic neuralgia.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep can also contribute to a stronger immune system, thus lowering the risk of shingles.
Conclusion
Shingles is more than just a painful skin condition; it can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Awareness of its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is vital for anyone, especially those over the age of 50. By taking preventive measures and seeking prompt medical attention, individuals can manage the effects of shingles more effectively and reduce the risk of complications. If you suspect you may have shingles, do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support.