Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the difference between "acute" and "chronic bronchitis" is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Both forms of bronchitis involve inflammation of the bronchial tubes, but they differ significantly in their causes, symptoms, duration, and treatment options.
What is Acute Bronchitis?
"Acute bronchitis" is characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms and is usually caused by a viral infection, often following a cold or flu. The inflammation of the bronchial tubes leads to coughing, mucus production, fatigue, and sometimes wheezing. Acute bronchitis typically lasts for a few weeks and is often self-limiting, meaning it resolves on its own without severe medical intervention. Most patients recover completely, although coughing may persist for some time even after other symptoms have disappeared.
What is Chronic Bronchitis?
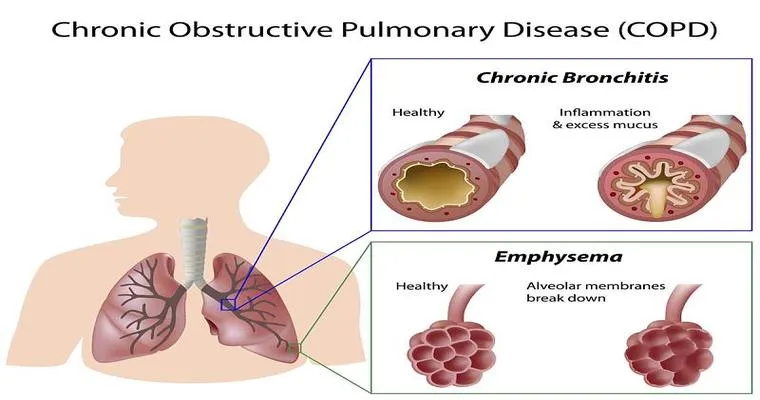
In contrast, "chronic bronchitis" is a long-term condition defined by a persistent cough that produces mucus for at least three months in two consecutive years. The main cause of chronic bronchitis is prolonged exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational dust. This form of bronchitis is part of a group of lung diseases known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Patients with chronic bronchitis often experience ongoing symptoms, including shortness of breath, frequent respiratory infections, and fatigue.
Key Differences Between Acute and Chronic Bronchitis
1. "Duration": Acute bronchitis is temporary and typically lasts less than three weeks, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition that persists for many months or even years.
2. "Causes": Acute bronchitis is usually caused by viral infections, whereas chronic bronchitis is primarily due to long-term exposure to irritants.
3. "Symptoms": While both types share common symptoms such as coughing and mucus production, chronic bronchitis is characterized by a more severe and prolonged cough, often accompanied by shortness of breath.
4. "Treatment": Treatment for acute bronchitis usually focuses on relieving symptoms, such as using cough suppressants and staying hydrated. On the other hand, chronic bronchitis may require long-term management strategies, including bronchodilators, steroids, and lifestyle changes like quitting smoking.
Conclusion
In summary, while both "acute" and "chronic bronchitis" involve inflammation of the bronchial tubes, they differ fundamentally in terms of duration, causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Recognizing these differences is essential for individuals experiencing respiratory symptoms to seek appropriate medical care and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you have bronchitis or are experiencing persistent respiratory issues, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and tailored treatment options.