Recent advancements in "stroke research" have shed light on critical aspects of prevention, treatment, and recovery. Strokes, which occur when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, continue to be a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. Understanding the latest findings can empower individuals to take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment. This article explores the most significant developments in "stroke prevention", "treatment options", and "rehabilitation techniques" based on the latest research.
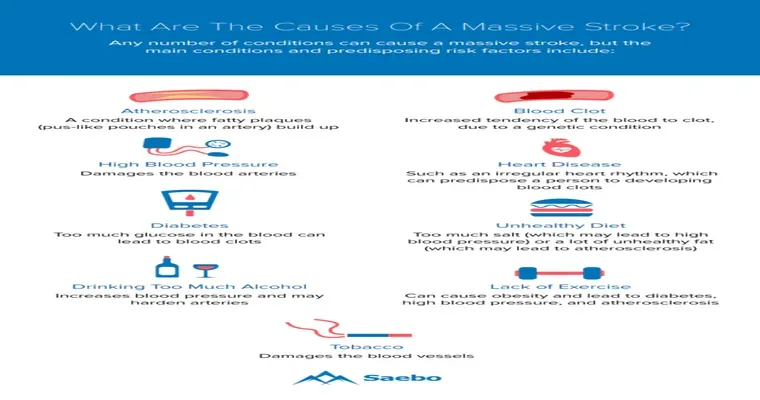
One of the most promising areas of "stroke prevention" research focuses on the role of lifestyle factors. Studies have shown that maintaining a "healthy diet", engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can significantly reduce the risk of having a stroke. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has been linked to lower stroke incidence. Additionally, researchers are investigating the impact of "sleep quality" on stroke risk, emphasizing the importance of adequate rest for overall brain health.
In terms of "treatment options", recent studies have highlighted the effectiveness of "thrombectomy" for certain types of strokes, particularly ischemic strokes caused by blood clots. Thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves removing the clot using specialized devices. Research indicates that patients who undergo this treatment within a specific time window experience better outcomes and reduced disability. Furthermore, advances in "thrombolytic therapy", which uses medication to dissolve blood clots, have improved treatment protocols, enabling faster response times in emergency situations.
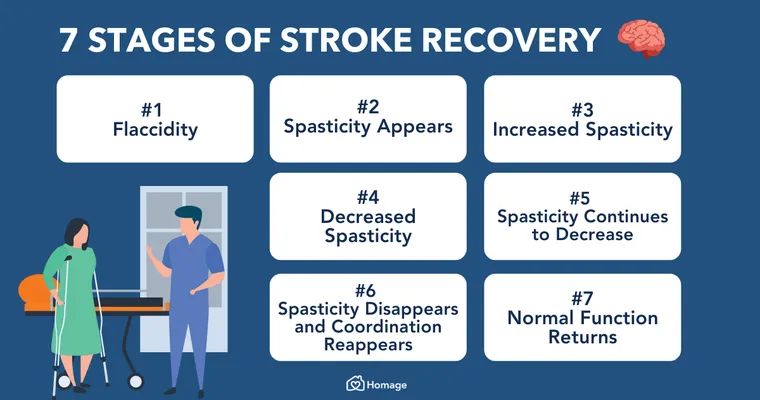
The field of "rehabilitation" has also seen significant progress. Innovative therapies, including robotic-assisted rehabilitation and virtual reality, are being explored to enhance recovery for stroke survivors. These technologies can provide individualized therapy, making the rehabilitation process more engaging and effective. Additionally, studies emphasize the importance of early intervention and multidisciplinary approaches, combining physical, occupational, and speech therapy to support comprehensive recovery.
Moreover, ongoing research is delving into the genetic and molecular factors that contribute to stroke risk. Understanding these elements could lead to the development of targeted interventions and personalized treatment plans. For instance, researchers are exploring biomarkers that could predict an individual's susceptibility to stroke, paving the way for preventive strategies tailored to specific risk profiles.
In conclusion, the latest research on strokes underscores the importance of understanding "stroke prevention", effective "treatment options", and innovative "rehabilitation techniques". By staying informed about these advancements, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their stroke risk and improve outcomes in the event of a stroke. Continued research in this field is essential for developing new strategies that could ultimately save lives and enhance the quality of life for stroke survivors.