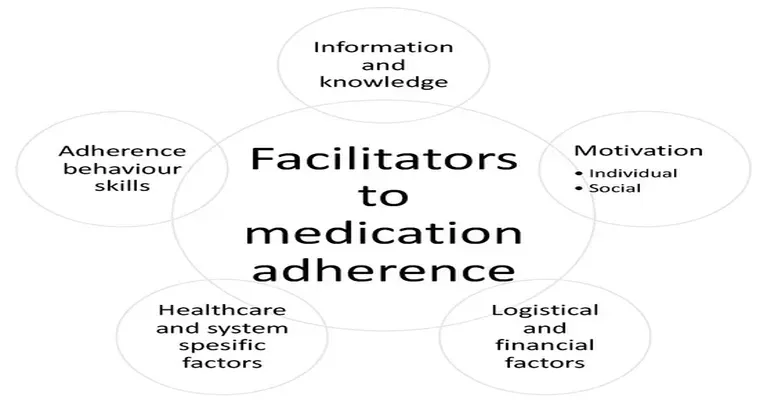
Medication adherence is a critical issue for "seniors" managing chronic conditions. Despite the availability of various treatments, many elderly individuals struggle with "following prescribed medication regimens". This can lead to serious health complications and increased healthcare costs. Understanding the top problems with medication adherence in seniors is essential for caregivers, healthcare providers, and family members aiming to improve health outcomes for this vulnerable population.
1. Complex Medication Regimens
One of the most significant challenges seniors face is the complexity of their medication regimens. Many older adults take multiple medications, often referred to as polypharmacy. This complexity can lead to confusion about dosages and schedules. When medications are not taken as directed, it can result in ineffective treatment or adverse drug interactions, ultimately jeopardizing the patient's health.
2. Cognitive Decline
Cognitive decline is another major factor affecting medication adherence in seniors. Conditions such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease can impair memory and decision-making abilities, making it difficult for seniors to remember when and how to take their medications. This cognitive impairment can lead to missed doses or incorrect usage, further complicating their medical conditions.
3. Physical Limitations
Many seniors experience physical limitations that can hinder their ability to manage medications effectively. Arthritis, vision problems, and other age-related conditions can make it challenging to open pill bottles, read labels, or even remember to take medications. As a result, seniors may skip doses or take medications incorrectly, leading to suboptimal health outcomes.
4. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
The side effects of medications can also discourage seniors from adhering to their treatment plans. Older adults may experience adverse reactions more severely than younger individuals, leading to discomfort or fear of taking their medications. This can cause them to stop taking prescribed medications altogether, which can exacerbate their underlying health issues.
5. Lack of Support and Communication
Effective communication between healthcare providers and seniors is crucial for medication adherence. Unfortunately, many seniors feel overwhelmed or intimidated during medical appointments, which can lead to misunderstandings about their medications. Additionally, a lack of support from family members or caregivers may leave seniors feeling isolated and less likely to adhere to their medication regimens.
6. Financial Constraints
Financial issues can significantly impact a senior's ability to maintain medication adherence. Many elderly individuals are on fixed incomes and may struggle to afford their medications. High prescription drug costs can lead to skipped doses or the decision to forgo medications altogether. This financial burden can have serious implications for their health, ultimately resulting in increased medical expenses due to complications from untreated conditions.
Conclusion
Addressing the "problems with medication adherence in seniors" is vital to improving their health and quality of life. By recognizing the challenges they face—such as complex regimens, cognitive decline, physical limitations, side effects, lack of support, and financial constraints—caregivers and healthcare providers can implement strategies to help seniors manage their medications more effectively. This might include simplifying medication schedules, offering assistance with organization, ensuring open lines of communication, and exploring financial aid options. By taking these steps, we can foster better health outcomes for our senior population.