Arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to "joint pain", stiffness, and inflammation. Understanding how to effectively manage and treat arthritis is crucial for improving quality of life. This article will explore various methods for "treating arthritis", focusing on lifestyle changes, medication options, and alternative therapies that can help alleviate joint pain.
Understanding Arthritis
Arthritis encompasses over 100 different types of inflammatory joint diseases, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most prevalent. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that interferes with daily activities. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing the condition effectively.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Joint Pain
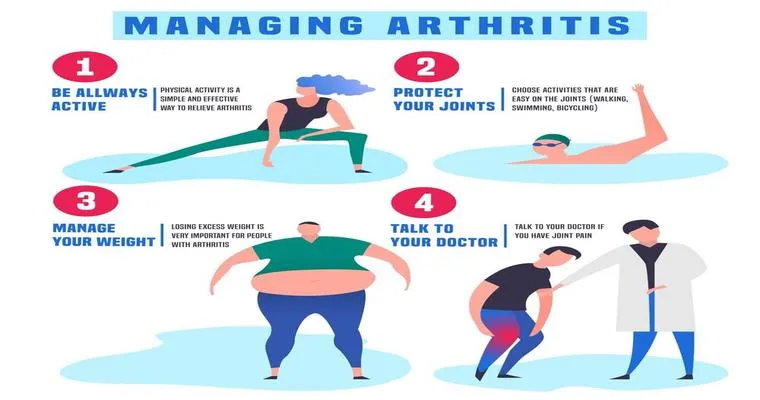
1. "Maintain a Healthy Weight": Excess weight places additional stress on your joints, especially the knees, hips, and back. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce joint pain and improve mobility.
2. "Stay Active": Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining joint function and reducing stiffness. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking can help strengthen the muscles around the joints without causing undue stress.
3. "Balanced Diet": Consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage arthritis symptoms. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon and walnuts. Foods high in sugar and processed fats should be limited as they can exacerbate inflammation.
4. "Hydration": Staying well-hydrated is essential for joint health. Water helps lubricate joints and can prevent stiffness. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, or more if you are active.
Medical Treatments for Arthritis
1. "Over-the-Counter Medications": Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen can provide temporary relief from joint pain and inflammation. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication.
2. "Prescription Medications": For more severe cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications such as corticosteroids or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These can help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of arthritis.
3. "Physical Therapy": A physical therapist can design a customized exercise program tailored to your individual needs. They can also teach you techniques to protect your joints and improve mobility.
4. "Surgery": In some cases, surgical options may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints. This is typically considered when other treatments have failed to provide relief.
Alternative Therapies
1. "Acupuncture": This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Many patients report reduced pain and improved function after acupuncture sessions.
2. "Massage Therapy": Regular massage can help relieve tension in the muscles surrounding the joints, improving circulation and promoting relaxation.
3. "Heat and Cold Therapy": Applying heat can help relax tense muscles and improve circulation, while cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain. Alternating between hot and cold treatments can provide additional relief.
4. "Supplements": Some people find relief from joint pain with dietary supplements such as glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids. Consult with a healthcare provider before adding any new supplements to your regimen.
Conclusion
Treating arthritis and managing "joint pain" requires a multi-faceted approach that includes lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and alternative therapies. By taking proactive steps and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with arthritis can find effective strategies to alleviate pain and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, early intervention is key, so don’t hesitate to seek help if you experience persistent joint discomfort.