Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, commonly referred to as "COPD", is a progressive lung condition that causes breathing difficulties and reduces the quality of life for millions of individuals worldwide. Effective "COPD treatments" are essential for managing symptoms, improving lung function, and enhancing overall wellbeing. This article explores various treatment options available for COPD, including medications, lifestyle changes, and advanced therapies.
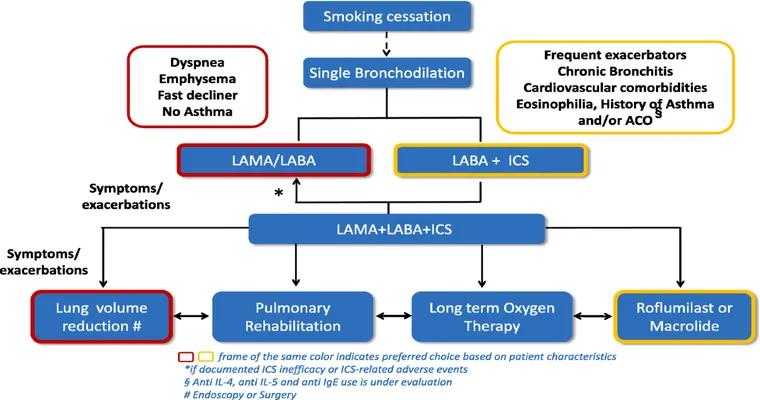
One of the primary goals in the management of COPD is to relieve symptoms and prevent exacerbations. "Bronchodilators" are commonly prescribed medications that help relax the muscles around the airways, allowing for easier breathing. These can be categorized into short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators. Short-acting bronchodilators provide quick relief during acute episodes, while long-acting versions are used for ongoing control of symptoms.
In addition to bronchodilators, "inhaled corticosteroids" are often recommended to reduce inflammation in the airways. These medications can be particularly helpful for those who experience frequent flare-ups. Combining inhaled corticosteroids with bronchodilators can lead to improved lung function and a decrease in the frequency of exacerbations.
For patients with advanced COPD, "oxygen therapy" may be necessary. This treatment involves using supplemental oxygen to ensure adequate oxygen levels in the blood, especially during exercise or sleep. It can significantly improve the quality of life for those with severe oxygen deficiency.
Another key aspect of COPD management is pulmonary rehabilitation. This comprehensive program includes exercise training, nutritional counseling, and education on managing the condition. "Pulmonary rehabilitation" has been shown to enhance physical fitness, increase endurance, and even lead to a reduction in hospitalizations.
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing COPD. Quitting smoking is the most significant step one can take to slow the progression of the disease. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to overall lung health. Patients are encouraged to work closely with healthcare providers to create a personalized action plan that includes these lifestyle modifications.
For some patients, surgical options may be considered. "Lung volume reduction surgery" removes damaged lung tissue, allowing the remaining healthy lung tissue to function more efficiently. In select cases, a "lung transplant" may be an option for individuals with end-stage COPD, providing a chance for a better quality of life.
In conclusion, the treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual needs of each patient. From medications such as bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids to lifestyle changes and advanced therapies, effective management of COPD can lead to improved symptoms and a better quality of life. Working closely with healthcare professionals is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan that addresses the unique challenges posed by this chronic condition.