Depression in the elderly is a significant public health concern that affects millions of older adults. Understanding the "symptoms of depression", its "causes", and the various "treatment options" available is crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected. As we age, the risk of developing depression increases, often due to factors such as "loss of loved ones", "chronic illness", or "social isolation". Fortunately, there are effective treatments for depression in the elderly that can help restore emotional well-being.
Understanding Depression in the Elderly
Depression in older adults can manifest differently than in younger populations. Symptoms may include persistent sadness, withdrawal from social activities, changes in appetite, and difficulty concentrating. It is essential to recognize these signs early, as untreated depression can lead to worsening health conditions and a decline in overall well-being.
Common Treatment Options
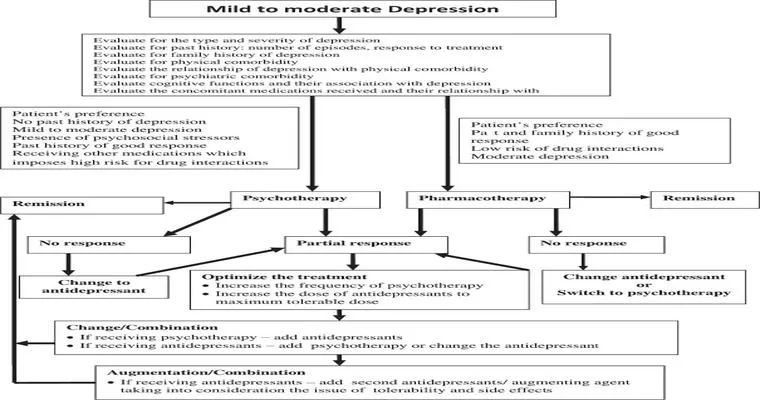
1. "Psychotherapy": One of the most effective treatments for depression in the elderly is psychotherapy, particularly "cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)". This form of therapy helps individuals identify negative thought patterns and replace them with healthier, more positive ones. Other therapeutic approaches, such as "interpersonal therapy", can also be beneficial.
2. "Medication": Antidepressant medications, such as "selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)", are commonly prescribed for older adults experiencing depression. These medications can help balance chemicals in the brain that affect mood. However, it is essential for elderly patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor for potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
3. "Lifestyle Changes": Encouraging a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact the treatment of depression in the elderly. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and social engagement can contribute to improved mood and overall health. Activities such as walking, gardening, and participating in community events can foster social connections and reduce feelings of isolation.
4. "Support Groups": Connecting with others who understand the challenges of depression can be incredibly beneficial. Support groups provide a safe space for sharing experiences and coping strategies. Many communities offer groups specifically for older adults, focusing on issues unique to this age group.
5. "Alternative Therapies": Some elderly individuals may find relief from depression through alternative therapies such as "mindfulness meditation", "yoga", or "art therapy". These approaches can enhance emotional well-being and provide new outlets for expression and connection.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Approach
A comprehensive approach to treating depression in the elderly is crucial. It is essential to consider each individual's unique circumstances, including their medical history, support system, and personal preferences. Collaboration among healthcare providers, caregivers, and family members can ensure that the elderly receive the most effective and personalized care possible.
Conclusion
Treating depression in the elderly requires an understanding of the unique challenges faced by this population. By recognizing the symptoms and exploring various "treatment options", including psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and support groups, we can help older adults lead happier and more fulfilling lives. It is vital to approach treatment holistically, involving healthcare professionals and loved ones to provide the best possible support. If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, seeking help is the first step toward recovery.