Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the most serious "complications" associated with this disease is kidney damage, often referred to as "diabetic nephropathy". Understanding the connection between "type 2 diabetes" and kidney health is crucial for prevention and management. This article will explore the implications of diabetes on kidney function, the warning signs of kidney complications, and effective strategies for maintaining renal health.
Understanding Kidney Complications in Type 2 Diabetes
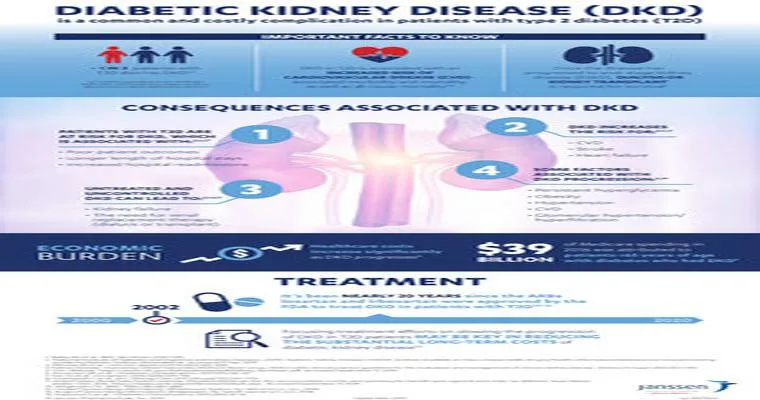
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products from the blood, regulating fluid balance, and maintaining electrolyte levels. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to a decline in their ability to function properly. Over time, this can progress to "chronic kidney disease (CKD)", and in severe cases, it may necessitate "dialysis" or kidney transplantation.
Risk Factors for Kidney Damage
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing kidney complications in those with type 2 diabetes. These include:
"Poor blood sugar control": Consistently high blood sugar levels can exacerbate kidney damage.
"High blood pressure": Hypertension is common in people with diabetes and can further strain the kidneys.
"High cholesterol": Elevated cholesterol levels can contribute to the hardening of blood vessels, impacting kidney function.
"Family history": A genetic predisposition may increase the risk of developing kidney complications.
Warning Signs of Kidney Complications
Early detection of kidney issues is essential for effective management. Some warning signs that may indicate kidney complications include:
Swelling in the feet, ankles, or around the eyes
Changes in urine output, such as increased frequency or foamy urine
Fatigue or weakness
Nausea and vomiting
Persistent itching
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Preventing Kidney Complications
There are several proactive steps individuals with type 2 diabetes can take to protect their kidneys:
1. "Manage blood sugar levels": Keeping blood sugar within the target range can significantly reduce the risk of kidney damage. This can be achieved through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medication if necessary.
2. "Monitor blood pressure": Regularly checking blood pressure and keeping it within a healthy range is critical. Lifestyle changes, such as reducing sodium intake and increasing physical activity, can help manage hypertension.
3. "Maintain a healthy diet": A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and reduce the risk of complications. Limiting processed foods and sugars is also beneficial.
4. "Stay hydrated": Drinking plenty of water helps maintain proper kidney function and aids in flushing out toxins from the body.
5. "Regular check-ups": Routine screenings for kidney function, including urine tests and blood tests to measure creatinine levels, can help detect issues early on.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious "kidney complications", but with proper management and proactive measures, individuals can reduce their risk significantly. Maintaining healthy blood sugar and blood pressure levels, adopting a balanced diet, and being aware of the warning signs are essential steps in protecting kidney health. By prioritizing these factors, those living with type 2 diabetes can lead healthier lives and minimize the risk of kidney-related issues.