"Coronary artery disease" (CAD) is a significant health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the "coronary arteries", which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked, primarily due to atherosclerosis. This condition can lead to serious complications, including heart attacks and heart failure. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for coronary artery disease is crucial for effective management and prevention.
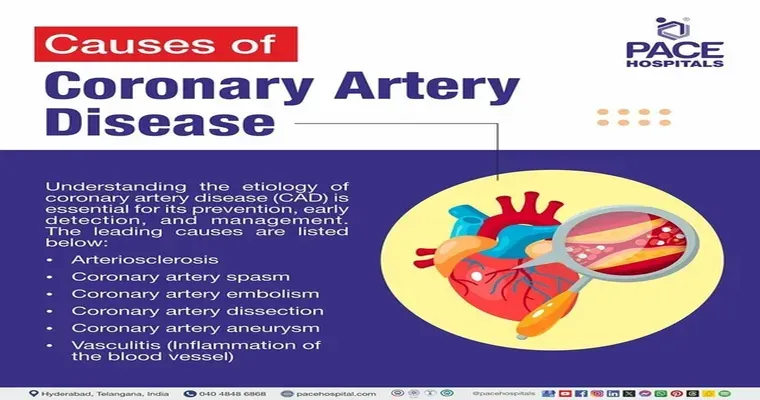
What Causes Coronary Artery Disease?
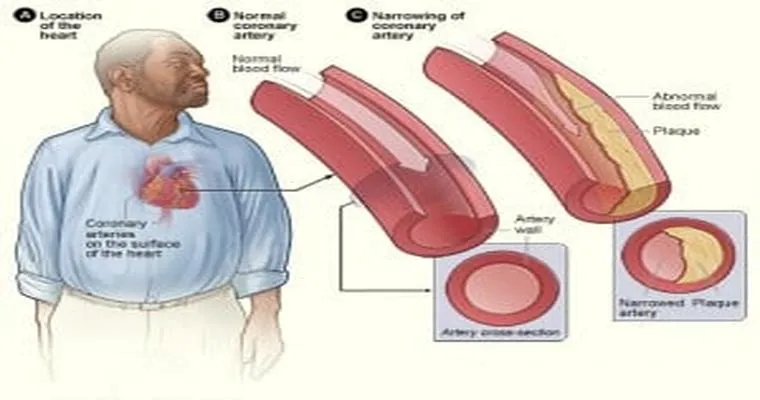
The primary cause of coronary artery disease is the buildup of "plaque" in the coronary arteries. Plaque consists of fat, cholesterol, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, this buildup can harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. Several risk factors contribute to the development of CAD, including:
1. "High cholesterol levels": Elevated levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol can increase the risk of plaque formation.
2. "Hypertension": High blood pressure can damage arteries and accelerate the development of atherosclerosis.
3. "Smoking": Tobacco use is a significant risk factor that damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen in the blood.
4. "Diabetes": High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of CAD.
5. "Obesity": Excess weight can lead to high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, all contributing to CAD.
6. "Sedentary lifestyle": Lack of physical activity increases the risk of developing CAD and its risk factors.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Many individuals with coronary artery disease may not experience symptoms until the condition has progressed significantly. Common symptoms include:
"Chest pain or discomfort": Often described as pressure, squeezing, or fullness in the chest.
"Shortness of breath": May occur with or without chest pain.
"Fatigue": Unusual tiredness during physical activity can be a sign of CAD.
"Heart palpitations": Irregular heartbeats may indicate underlying heart issues.
Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease
If CAD is suspected, healthcare providers may recommend several diagnostic tests to assess heart health, including:
"Electrocardiogram (ECG)": Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
"Stress test": Evaluates how the heart performs under physical stress.
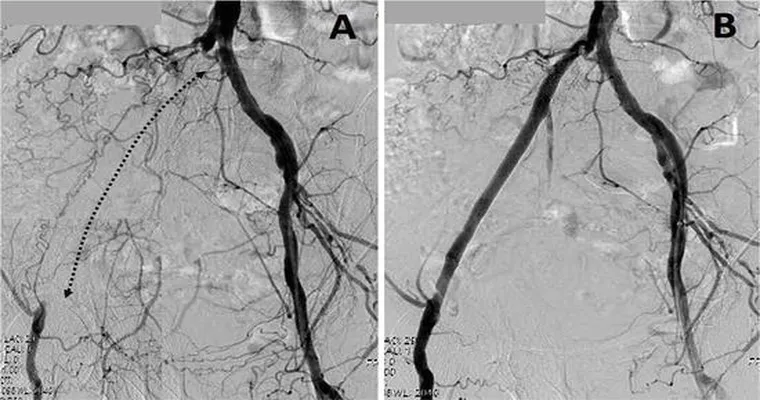
"Coronary angiography": Uses imaging to visualize the coronary arteries and identify blockages.
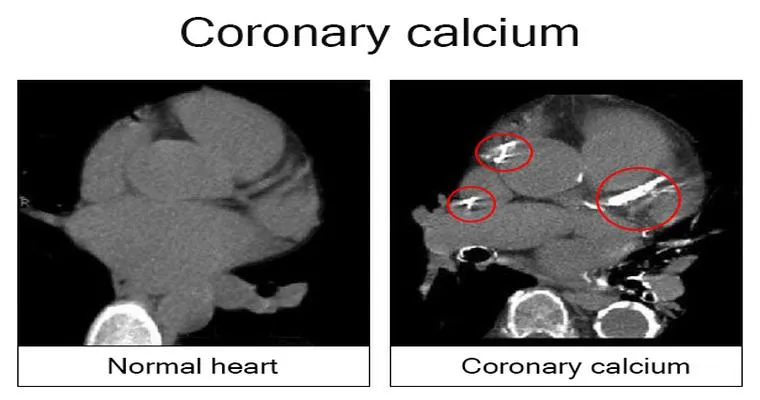
"CT coronary angiogram": A non-invasive imaging test that can detect coronary artery disease.
Treatment Options for Coronary Artery Disease
Treatment for CAD may vary based on the severity of the disease and the individual's overall health. Common treatment approaches include:
"Lifestyle changes": Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress can significantly impact overall heart health.
"Medications": Doctors may prescribe medications to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, prevent blood clots, and manage diabetes.
"Surgical interventions": In severe cases, procedures such as angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
Preventing Coronary Artery Disease
Preventing coronary artery disease involves addressing the modifiable risk factors. Some effective strategies include:
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
Regularly monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Managing diabetes effectively with the help of healthcare providers.
Staying physically active with at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
Conclusion
Understanding coronary artery disease is essential for prevention and management. By recognizing the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their heart health. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing CAD and improve overall well-being.