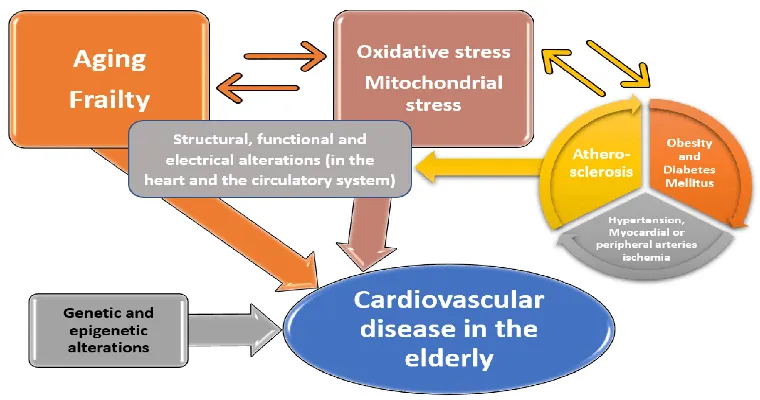
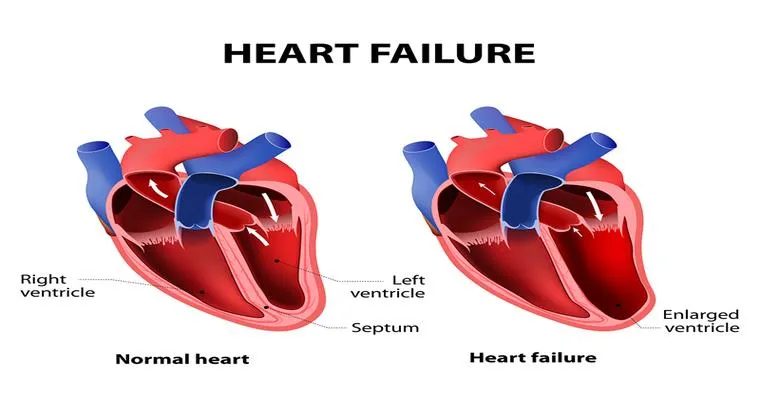
Heart failure is a "serious medical condition" that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly the "elderly population". As individuals age, the risk of developing heart-related issues increases, making it vital to understand the symptoms, causes, and management of heart failure in older adults. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of heart failure, including its types, risk factors, and treatment options tailored specifically for the elderly.
What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients reaching the body's organs. This condition can result from various underlying issues, such as "coronary artery disease", high blood pressure, or previous heart attacks. In older adults, the heart's ability to function may decline due to age-related changes, making them more susceptible to heart failure.
Types of Heart Failure
Heart failure can be classified into two main types: "systolic heart failure" and "diastolic heart failure". Systolic heart failure occurs when the heart's pumping ability is weakened, while diastolic heart failure happens when the heart cannot relax properly, leading to inadequate filling. Understanding these types is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment in elderly patients.
Risk Factors for Heart Failure in the Elderly
Several factors contribute to the development of heart failure in older adults. Some of the most significant risk factors include:
1. "Age": The likelihood of developing heart failure increases significantly with age.
2. "Hypertension": High blood pressure can cause the heart to work harder, leading to heart failure over time.
3. "Coronary artery disease": Blocked arteries can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle, increasing the risk of heart failure.
4. "Diabetes": This condition can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart.
5. "Obesity": Carrying excess weight can strain the heart, making it more susceptible to failure.
Symptoms of Heart Failure in the Elderly
Recognizing the symptoms of heart failure is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms experienced by the elderly include:
"Shortness of breath" during daily activities or while lying down
"Fatigue" and weakness
"Swelling" in the legs, ankles, or abdomen due to fluid retention
"Rapid or irregular heartbeat"
"Coughing or wheezing" that may produce pink, frothy mucus
If these symptoms are observed, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and potential treatment.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing heart failure typically involves a combination of physical exams, medical history assessments, and diagnostic tests such as echocardiograms, blood tests, and chest X-rays. Once diagnosed, treatment options for heart failure in the elderly may include:
"Medications": Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta-blockers are commonly prescribed to help manage heart failure symptoms and improve heart function.
"Lifestyle changes": Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking can significantly impact heart health.
"Monitoring and follow-up": Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for managing heart failure and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Understanding heart failure in the elderly is crucial for early detection and effective management of this condition. By recognizing the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options available, both patients and caregivers can work together to improve the quality of life for older adults living with heart failure. Prioritizing heart health through lifestyle changes and regular medical care can lead to better outcomes and a healthier future for the elderly population.