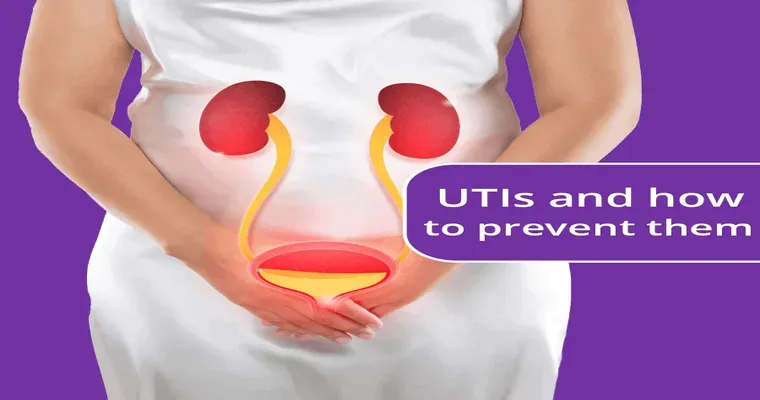
A "Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)" is a common medical condition that affects millions of people each year. It occurs when harmful bacteria enter the urinary system, leading to inflammation and infection. Common symptoms of a UTI include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for UTIs is crucial for effective management and prevention.
What Causes a UTI?
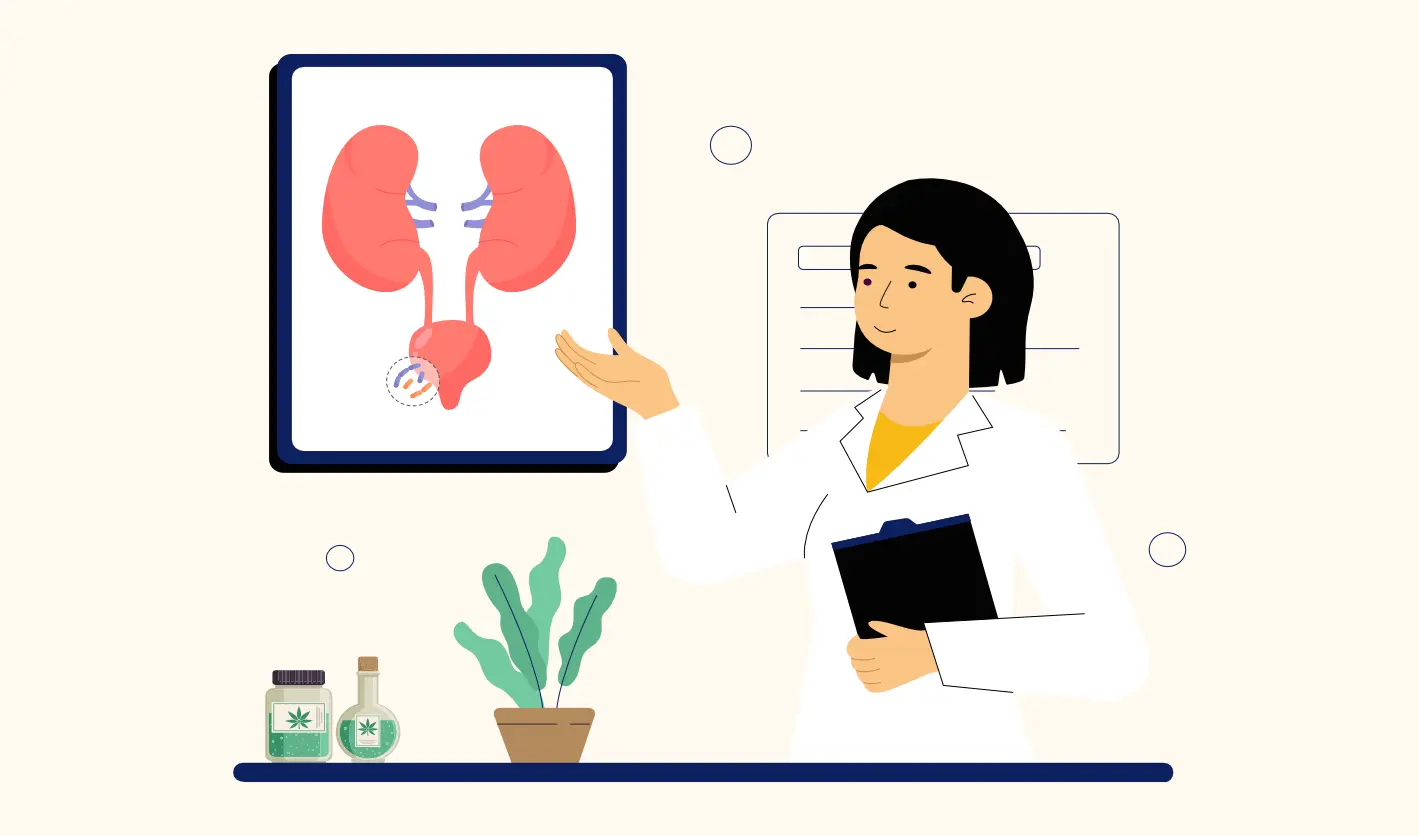
UTIs can be caused by various factors, but the most common culprit is bacteria entering the urinary tract. The most frequent type of bacteria responsible for UTIs is "Escherichia coli (E. coli)", which naturally resides in the intestines. Other factors that may contribute to the risk of developing a UTI include:
Sexual activity: Increased activity can lead to bacterial transfer.
Certain birth control methods: Diaphragms and spermicides can irritate the urinary tract.
Hormonal changes: Fluctuations during menstruation or menopause can affect the urinary system.
Urinary retention: Inability to fully empty the bladder can create an environment for bacteria to thrive.
Recognizing UTI Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of a UTI early can lead to prompt treatment and relief. Some common symptoms include:
- A "strong, persistent urge" to urinate
- A "burning sensation" during urination
- Frequent urination with only small amounts of urine
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, particularly in women
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing a UTI typically involves a "urinalysis", where a sample of urine is tested for the presence of bacteria, blood, or pus. In some cases, a "urine culture" may be performed to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection.

Treatment options for UTIs generally include:
Antibiotics: The most common treatment for UTIs, antibiotics help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. The type and duration of antibiotics prescribed may vary based on the severity of the infection and individual health factors.
Pain relief medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort while the body fights the infection.
Increased fluid intake: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Prevention Tips
Preventing UTIs is often possible with some lifestyle changes and habits. Here are a few effective prevention tips:
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush out bacteria.
Practice good hygiene: Wipe from front to back after using the toilet and urinate after sexual intercourse to reduce bacterial transfer.
Avoid irritants: Stay clear of irritating feminine products, such as douches and powders, that can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria.
Consider dietary changes: Some studies suggest that cranberry juice may help prevent UTIs due to its ability to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract.
Conclusion
Understanding "UTIs", their symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for maintaining urinary health. If you suspect you have a UTI, seeking medical attention promptly can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. By adopting preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing urinary tract infections in the future.