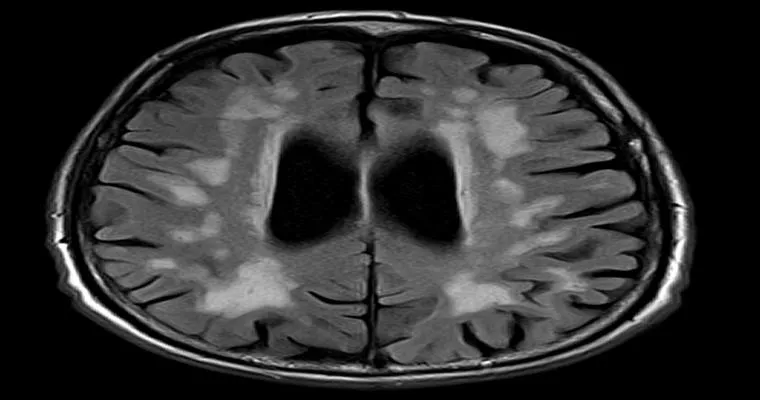
"Multi-Infarct Dementia" is a type of "vascular dementia" that results from multiple small strokes or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) in the brain. This condition is characterized by the progressive decline in cognitive function due to the accumulation of damage caused by these strokes. Unlike other forms of dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease, which can have a more gradual onset, Multi-Infarct Dementia typically has a more abrupt progression, often correlated with the occurrence of strokes.
Understanding the Causes
The primary cause of Multi-Infarct Dementia is insufficient blood flow to the brain, leading to the death of brain cells. This can happen due to various factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Risk factors such as "smoking", "high cholesterol", and a sedentary lifestyle can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing strokes, which may contribute to the development of this form of dementia.
Symptoms of Multi-Infarct Dementia
Symptoms of Multi-Infarct Dementia can vary widely among individuals, depending on the areas of the brain affected by the strokes. Common symptoms include:
Memory loss
Confusion
Difficulty concentrating
Changes in mood or behavior
Impaired judgment
These symptoms may appear suddenly, often after a stroke or TIA, and can fluctuate over time. It's essential for caregivers and family members to recognize these changes and seek medical advice promptly.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing Multi-Infarct Dementia typically involves a comprehensive evaluation that includes a medical history, neurological examinations, and imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans. These tests help identify areas of the brain affected by strokes.
While there is no cure for Multi-Infarct Dementia, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further strokes. This may involve:
Medications to control blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking
Cognitive therapy to help improve memory and cognitive function
Prognosis and Prevention
The prognosis for individuals with Multi-Infarct Dementia can vary. Some may experience a gradual decline in cognitive function, while others may have more sudden changes. Preventative measures are crucial for those at risk. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing chronic conditions, and regular medical check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of strokes and the subsequent development of Multi-Infarct Dementia.
Conclusion
Understanding "Multi-Infarct Dementia" is vital for early detection and effective management. By recognizing the symptoms and risk factors associated with this condition, individuals and their families can take proactive steps to maintain cognitive health and improve quality of life. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough assessment and personalized care plan.