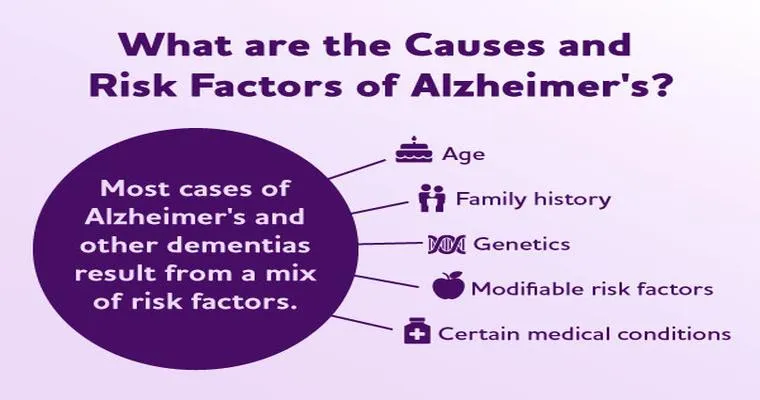
Dementia is a complex and debilitating condition characterized by a decline in cognitive function that significantly interferes with daily life. Understanding the "cause of dementia" is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. There are various types of dementia, each with its own underlying causes, but common factors include "Alzheimer's disease", "vascular issues", head injuries, and other health conditions that affect brain function.
One of the most prevalent forms of dementia is "Alzheimer's disease", which accounts for approximately 60 to 80 percent of all dementia cases. The exact cause of Alzheimer's remains unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Researchers have identified specific proteins, such as "amyloid plaques" and "tau tangles", that accumulate in the brains of those with Alzheimer's, leading to neuronal damage and cognitive decline.
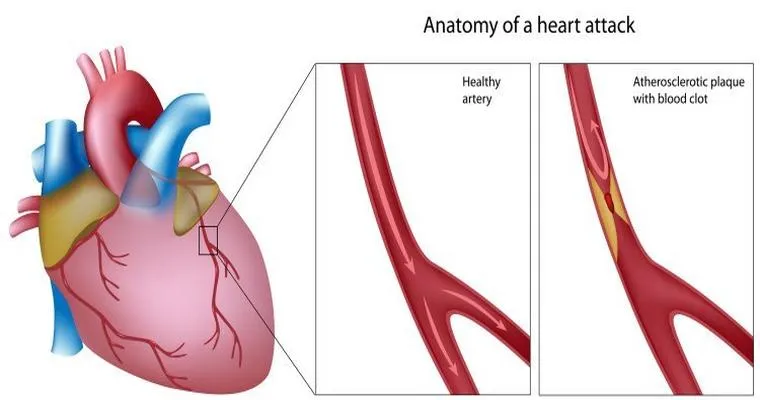
Another significant cause of dementia is "vascular dementia", which occurs due to impaired blood flow to the brain. This can result from conditions like "stroke", high blood pressure, or diabetes. When the brain does not receive adequate oxygen and nutrients, it can lead to cognitive impairment and memory loss. Managing cardiovascular health is crucial in reducing the risk of vascular dementia.
Other causes of dementia can include "frontotemporal dementia", which primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in personality and behavior. This type of dementia can be linked to genetic mutations and is often diagnosed at a younger age compared to Alzheimer's disease.
Additionally, certain medical conditions can contribute to dementia-like symptoms. For instance, "Parkinson's disease" and "Huntington's disease" can lead to cognitive decline over time. Moreover, untreated "depression", "thyroid problems", and "vitamin deficiencies" can also mimic dementia symptoms, highlighting the importance of comprehensive medical evaluations.
In conclusion, the "cause of dementia" is multifaceted and can vary significantly from person to person. While age is a significant risk factor, understanding the various types and associated conditions can help in early detection and management. Ongoing research continues to explore the complex interplay of genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors that contribute to this challenging condition. If you or a loved one are experiencing cognitive changes, it is essential to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause and explore potential treatment options.