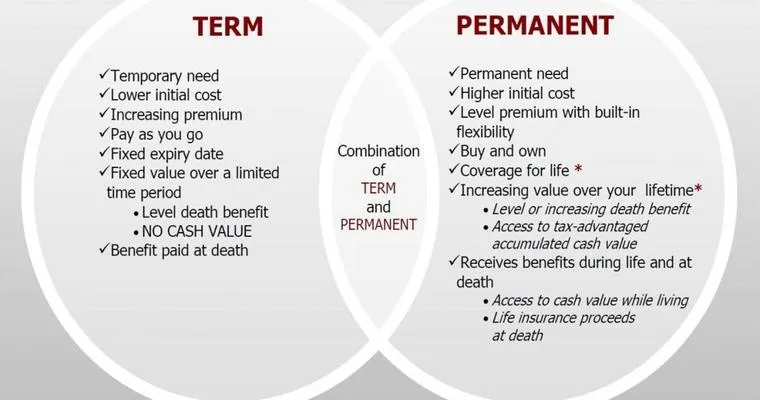
When considering life insurance, it's crucial to understand the "essential differences" between "permanent" and "term life insurance". Both types serve the purpose of providing financial protection for your loved ones, but they do so in different ways. This article will explore these differences to help you make an informed decision.
1. Duration of Coverage
The most significant difference between "permanent" and "term life insurance" is the duration of coverage. "Term life insurance" provides coverage for a specified period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. If the insured passes away during this period, the beneficiaries receive the death benefit. In contrast, "permanent life insurance" offers lifelong coverage, meaning as long as premiums are paid, your beneficiaries will receive a payout regardless of when you pass away.
2. Premium Structure
Another crucial distinction lies in the "premium structure". "Term life insurance" generally comes with lower initial premiums, making it more affordable for many individuals. However, these premiums can increase upon renewal after the term ends. On the other hand, "permanent life insurance" typically involves higher premiums, but they remain level throughout the insured's life. This can make "permanent policies" more predictable in terms of budgeting.
3. Cash Value Component
One of the unique features of "permanent life insurance" is the "cash value component". A portion of the premiums paid goes into a cash value account that grows over time, often at a guaranteed rate. This cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing a financial resource during the policyholder's lifetime. In contrast, "term life insurance" does not accumulate cash value, meaning you only receive the death benefit if the policyholder passes away during the term.
4. Flexibility
"Term life insurance" offers less flexibility compared to "permanent policies". Once the term expires, the coverage ends, and renewal may come with higher premiums or limited options based on health changes. Conversely, "permanent life insurance" often allows for more flexibility, such as adjusting premium payments and death benefits, depending on the policy type.
5. Purpose and Use
The intended purpose of the two types of insurance also varies significantly. "Term life insurance" is typically used to cover specific financial responsibilities, such as a mortgage or children's education, during a particular time frame. It is ideal for those seeking temporary coverage at a lower cost. "Permanent life insurance", however, is often used as a long-term financial strategy, serving not only as a death benefit but also as an investment tool for wealth accumulation and estate planning.
6. Complexity of Policies
Finally, the complexity of policies differs between "permanent" and "term life insurance". "Term life insurance" is straightforward, making it easier to understand. In contrast, "permanent life insurance" policies can be more complex, with various options, riders, and investment components. This complexity may require more time and research to fully comprehend the benefits and limitations.
Conclusion
Understanding the "essential differences" between "permanent" and "term life insurance" is vital for making an informed decision tailored to your financial goals and needs. Whether you opt for the affordability and simplicity of "term life insurance" or the lifelong coverage and investment potential of "permanent life insurance", knowing these differences will help you choose the right policy for your situation. Take the time to evaluate your personal circumstances, and consider consulting with a financial advisor to determine the best route for securing your family's financial future.