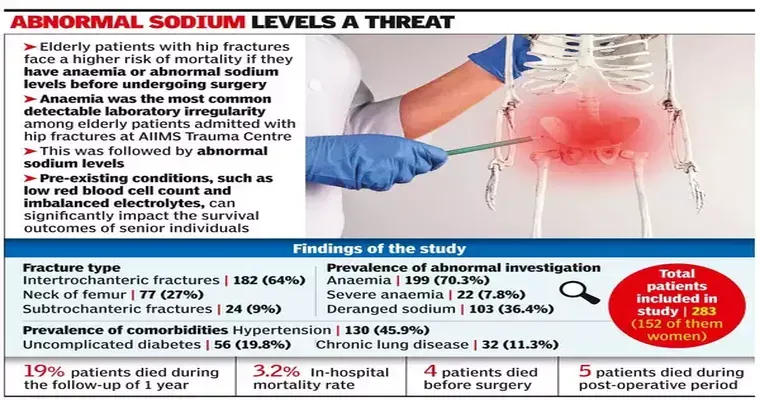
The "breaking of a hip" is a serious concern for "elderly women", significantly increasing their "risk of death" and complications. With age, bone density decreases, making falls more dangerous. Understanding the implications of a hip fracture can help in prevention and management strategies.
When an elderly woman experiences a "hip fracture", the consequences can be dire. Studies show that the mortality rate within the first year following a hip fracture can be as high as 20 to 30 percent. This statistic highlights the severity of the injury and the associated health risks. Post-fracture complications, such as "infection", "blood clots", and "pneumonia", often contribute to this increased mortality rate.
The reasons behind the elevated risk of death in elderly women following a hip fracture are multifaceted. First, many women in this age group already face a decline in overall health, which can be exacerbated by the stress of a major injury. The "surgery" required to repair a fractured hip, often involving a "hip replacement", can lead to further complications in individuals with existing health issues. Additionally, the "rehabilitation process" can be challenging, as many elderly individuals may struggle with mobility, leading to prolonged periods of immobility and associated risks.
Preventing falls is crucial in reducing the incidence of hip fractures among elderly women. Simple measures such as maintaining a safe living environment, regular exercise to strengthen muscles and improve balance, and routine health checks can make a significant difference. Furthermore, medical assessments for osteoporosis can help identify women at higher risk for fractures, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
In conclusion, the "breaking of a hip" significantly elevates the "risk of death" in elderly women, underscoring the need for awareness and preventive measures. Understanding the risks associated with hip fractures can encourage families and caregivers to take proactive steps in safeguarding the health of elderly women, ultimately improving their quality of life and longevity.